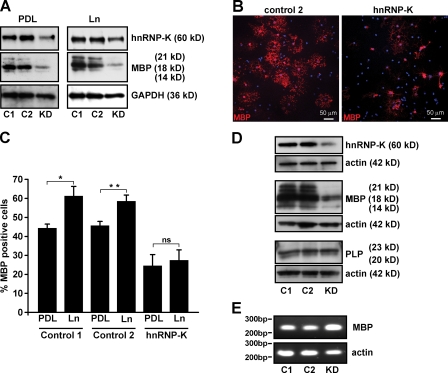
Figure 5.
hnRNP-K is required for laminin-induced MBP expression. (A) Western blot for hnRNP-K and MBP expression in oligodendrocytes after transfection with no (C1), nontargeting (C2), or hnRNP-K siRNA duplexes (KD), as indicated, using GAPDH as a loading control. (B) Immunocytochemistry for MBP in oligodendrocytes generated from OPCs transfected with nontargeting, (control 2) or hnRNP-K siRNA, as indicated. (C) Percentage of MBP-expressing cells after transfection with no (control 1), nontargeting (control 2), or hnRNP-K siRNA, and culturing for 3 d on PDL or laminin. Statistical significance was tested by one-way ANOVA followed by a Tukey’s multiple comparison test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. Note that laminin enhances the number of MBP+ cells in the control experiments, and that hnRNP-K knockdown both reduces the number of MBP+ cells and abolishes the laminin-mediated enhancement of MBP expression. (D) Western blotting for hnRNP-K, MBP, PLP, and actin on lysates from cells after transfection with no (C1), nontargeting (C2), or hnRNP-K siRNA duplexes (KD). Note that hnRNP-K siRNA reduces MBP expression, but has no effect on PLP or actin levels. (E) RT-PCR for MBP mRNA and actin mRNA after transfection with no (C1), nontargeting (C2), or hnRNP-K siRNA duplexes (KD). Note that the hnRNP-K knockdown has no effect on the levels of MBP mRNA.