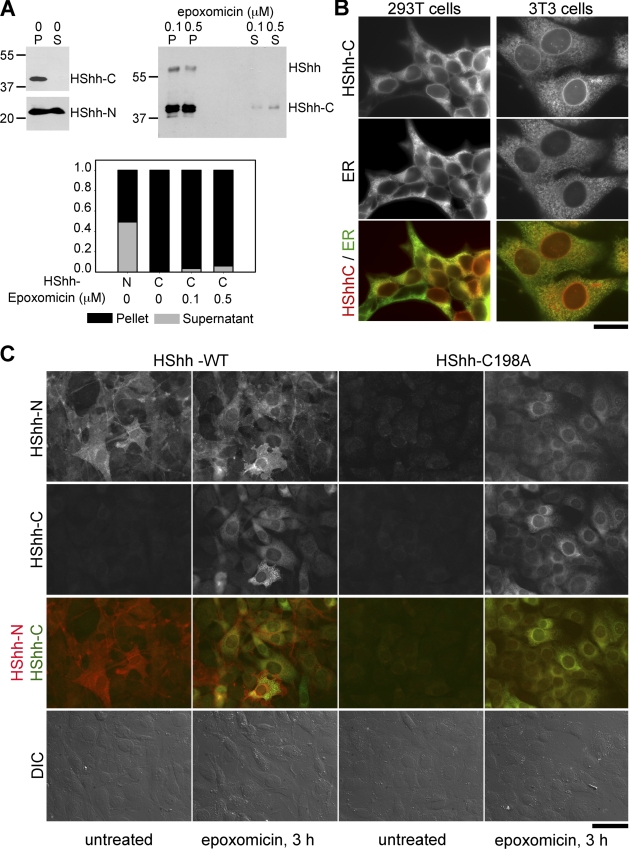
Figure 5.
HShh-C is not secreted and is degraded in the ER. (A) HShh-HA was stably expressed in 293T cells. The cells were washed and incubated for 12 h with DME containing 0.5% fetal bovine serum. The cell pellets and equivalent amounts of culture medium were analyzed for the presence of HShh-N and HShh-C by immunoblotting with HShh-N antibodies and HA antibodies. Where indicated, the proteasome inhibitor epoxomicin was present during the last 3 h of incubation. The graph shows the distribution of HShh-N and HShh-C between cells and medium. P, pellet. S, supernatant. Molecular masses are given in kilodaltons. (B) HShh was tagged with mCherry at its C terminus and stably expressed in 293T or in NIH-3T3 cells. Its localization was determined by fluorescence microscopy. The ER was revealed by immunostaining with rabbit antibodies against calnexin. The bottom row shows merged images. Bar, 20 µm. (C) Wild-type HShh-HA or the processing-defective mutant HShh-C198A-HA was stably expressed in NIH-3T3 cells. Cells were immunostained with rat HA and rabbit HShh-N antibodies followed by goat anti–rat Alexa Fluor 488 (green) and goat anti–rabbit Alexa Fluor 594 (red) secondary antibodies. The cells were incubated for 3 h with or without the proteasome inhibitor epoxomicin (1 µM). The third row shows merged images of the green and red channels. The bottom row shows differential interference contrast (DIC) images. Bar, 50 µm.