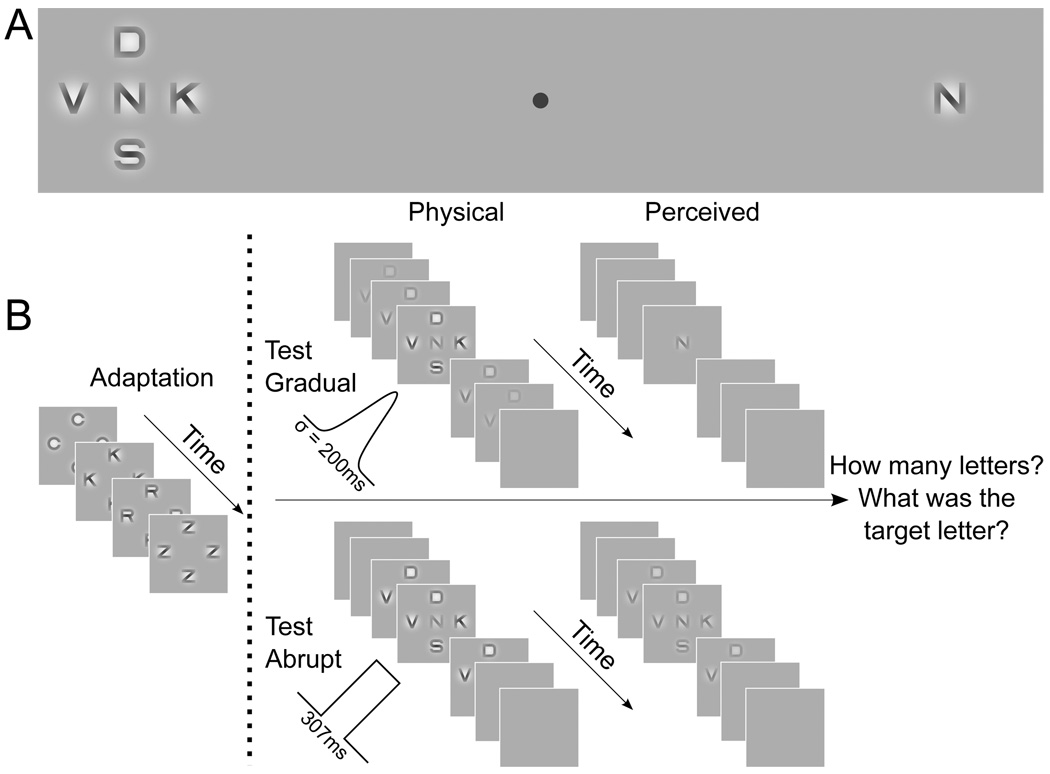
Figure 1. Crowding and identification task methods.
(A) A depiction of crowding. Fixate the central spot. The identity of the central letter on the left is difficult to distinguish, but the same letter can be easily identified when presented unflanked (right). (B) Experimental methods for the identification experiment. In adapt blocks, the flanker locations are adapted by letters updated at 10.7 Hz in random sequence. On gradual test presentations, the crowding array was smoothly ramped on and off over time (Gaussian contrast window with σ = 200ms). On abrupt tests, the crowding array was presented with abrupt onsets and offsets (square wave contrast window with duration 307 ms). In this example, five letters are presented; in the experiment, one (target only) to five (target and four flankers) letters were presented. After each trial, observers reported how many letters they saw and the identity of the target letter. See also Figure S1 for additional methods.