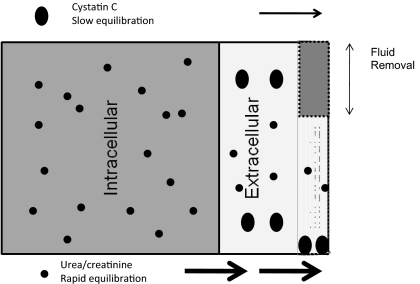
Figure 4.
Kinetic model of creatinine, urea, and cystatin C during hemodialysis. Cystatin C is a middle molecule that is distributed mainly extracellular and minimally protein bound. It was presumed to have slow redistribution between intravascular space and extravascular space because of its size. By contrast, urea and creatinine are distributed both in extracellular (both intra- and extravascular) and intracellular spaces, with presumed rapid equilibration between all three compartments during hemodialysis. As a result, it is presumed that small molecules are mostly affected by diffusive clearance and relatively unaltered by UF because of rapid equilibration. By contrast, CCRR is affected by a combination of diffusive and convective clearance and by ultrafiltration, which may concentrate the intravascular content of cystatin C.