Fig 3.
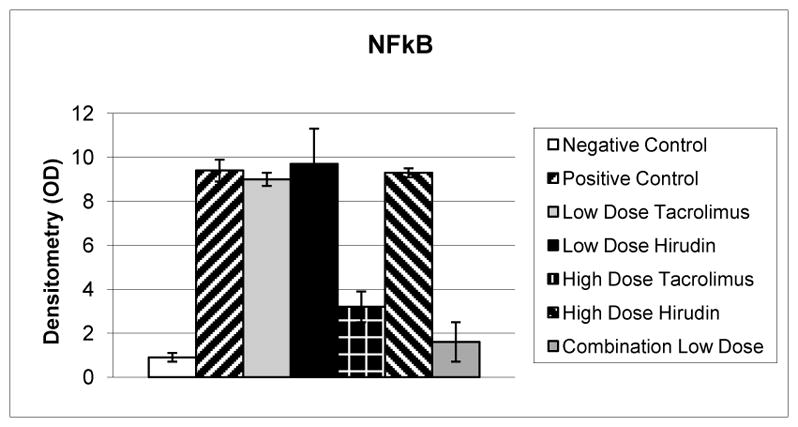
Relative optical densitometry (OD) of electromobility shift assay for nuclear factor kappa B (NFκB). Positive controls (n = 6) demonstrate a greater than tenfold increase in NFκB nuclear translocation compared with negative controls (p = 0.009, n = 4). Low-dose tacrolimus, low-dose hirudin, and high-dose hirudin therapy (n = 6 per group) did not significantly reduce NFκB translocation compared with positive controls (p = 0.2). High-dose tacrolimus therapy (n. 6) reduced NFκB translocation by 66% (p = 0.024) compared with positive controls. Low-dose combination therapy (n. 6) reduced NFκB translocation by 83% (p = 0.007) compared with positive controls.
