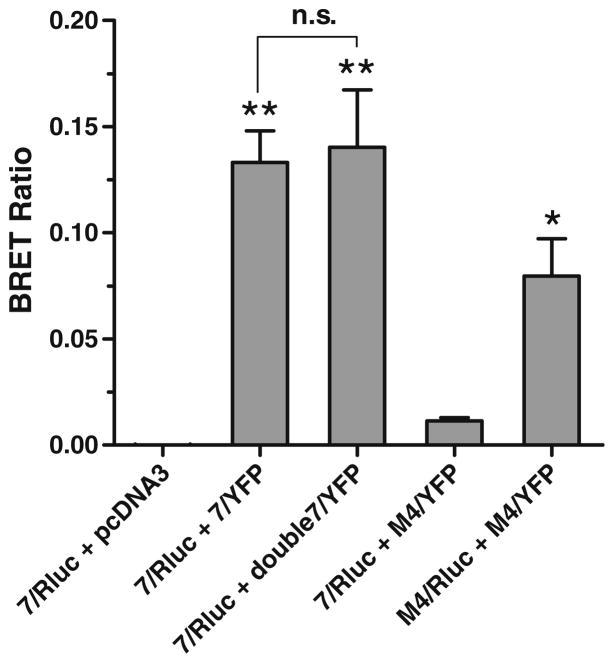
Fig. 7.
BRET assessment of h5-HT7 receptor homodimers in HEK-293 cells. Receptor constructs fusing Rluc or YFP onto the C-terminal tails of the h5-HT7 and muscarinic M4 receptors were synthesized, and combinations of these constructs were transiently transfected into HEK-293 cells. BRET ratios were calculated as described in the “Methods” section. A significant BRET signal was observed in cells co-transfected with equal quantities of h5-HT7/Rluc and h5-HT7/YFP receptor constructs. Doubling the expression of the BRET acceptor (h5-HT7/YFP) did not increase the BRET signal, which is consistent with a specific interaction between the h5- HT7 receptor constructs. Co-transfection of equal quantities of h5-HT7/Rluc and M4/YFP receptor constructs did not yield a significant BRET signal. This is consistent with the lack of specific interaction between these receptors. A significant BRET signal is observed between M4/Rluc and M4/YFP receptor constructs, indicating that the M4 receptor constructs can produce BRET. Taken together, these results indicate that h5-HT7 receptor exists as a homodimer in the h5-HT7 receptor-expressing HEK-293 cells. Results are the means±SEM of three independent experiments (*p<0.01, **p<0.001, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-test and “7/Rluc+pcDNA3” as control; n.s.p>0.05, unpaired t test)