TABLE 3.
Dichotomous Mixed-Effects Moderator Analyses of Treatment Versus Control Postintervention Comparisons: Meta-Analysis of Interventions to Increase Physical Activity (n = 74 852)
| Moderator | k0 | k1 | 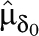 |
 |
SEdif | QB |
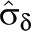 a a
|
I2 | Robustness |
| Source characteristics | … | ||||||||
| Publication status | 25 | 179 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.068 | 0.1 | 0.17 | 0.64 | … |
| Funding | 77 | 129 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.038 | 1.1 | 0.17 | 0.63 | … |
| Participant characteristics | … | ||||||||
| Previous exercisers | 88 | 118 | 0.27 | 0.14 | 0.036 | 13.3† | 0.16 | 0.60 | Poor |
| Mostly overweight | 22 | 58 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.062 | 0.2 | 0.15 | 0.51 | … |
| Research method characteristics | … | ||||||||
| Random assignment | 85 | 121 | 0.16 | 0.21 | 0.036 | 1.9 | 0.17 | 0.63 | … |
| Objective vs self-reported physical activity measure | 44 | 162 | 0.23 | 0.18 | 0.050 | 1.1 | 0.17 | 0.63 | … |
| Episodic vs overall physical activity measureb | 15 | 81 | 0.08 | 0.18 | 0.059 | 2.5 | 0.13 | 0.46 | … |
| Postintervention lag before measure | 15 | 104 | 0.39 | 0.18 | 0.083 | 6.3** | 0.14 | 0.45 | Poor |
| Intervention characteristics | … | ||||||||
| Social cognitive theory | 169 | 37 | 0.20 | 0.12 | 0.045 | 3.5* | 0.17 | 0.63 | Excellent |
| Transtheoretical model | 146 | 60 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.038 | 2.8* | 0.17 | 0.64 | Good |
| Social cognitive theory vs transtheoretical model | 41 | 18 | 0.14 | 0.08 | 0.065 | 0.9 | 0.14 | 0.54 | Poor |
| Access enhancement | 193 | 13 | 0.19 | 0.10 | 0.070 | 1.6 | 0.17 | 0.64 | … |
| Barriers management | 157 | 49 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.042 | 0.7 | 0.17 | 0.64 | … |
| Competitions or contests | 198 | 8 | 0.18 | 0.24 | 0.089 | 0.5 | 0.17 | 0.63 | … |
| Contracting | 197 | 9 | 0.19 | 0.08 | 0.082 | 1.7 | 0.17 | 0.64 | … |
| Consequences | 165 | 41 | 0.18 | 0.20 | 0.046 | 0.2 | 0.17 | 0.63 | … |
| Decision-making | 195 | 11 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.080 | 0.2 | 0.17 | 0.64 | … |
| Exercise prescription | 176 | 30 | 0.17 | 0.30 | 0.053 | 6.2** | 0.17 | 0.63 | Poor |
| Feedback | 165 | 41 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.043 | 0.0 | 0.17 | 0.63 | … |
| Fitness testing | 199 | 7 | 0.18 | 0.30 | 0.106 | 1.3 | 0.17 | 0.63 | … |
| Goal setting | 151 | 55 | 0.17 | 0.21 | 0.039 | 1.2 | 0.16 | 0.61 | … |
| Health education | 144 | 62 | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.039 | 0.6 | 0.17 | 0.63 | … |
| Mass media | 195 | 11 | 0.19 | 0.08 | 0.058 | 3.8* | 0.16 | 0.58 | Good |
| Modeling | 185 | 21 | 0.17 | 0.38 | 0.064 | 11.4† | 0.16 | 0.59 | Mixed |
| Monitoring | 170 | 36 | 0.17 | 0.24 | 0.049 | 1.9 | 0.17 | 0.63 | … |
| Motivational interviewing | 197 | 9 | 0.18 | 0.20 | 0.084 | 0.0 | 0.17 | 0.63 | … |
| Problem solving | 184 | 22 | 0.18 | 0.20 | 0.057 | 0.1 | 0.17 | 0.63 | … |
| Relapse prevention | 190 | 16 | 0.17 | 0.34 | 0.066 | 6.4** | 0.17 | 0.62 | Poor |
| Self-monitoring | 137 | 69 | 0.18 | 0.20 | 0.039 | 0.3 | 0.17 | 0.64 | … |
| Stimulus control | 191 | 15 | 0.19 | 0.14 | 0.067 | 0.6 | 0.17 | 0.64 | … |
| Supervised exercise | 172 | 34 | 0.17 | 0.29 | 0.055 | 4.8** | 0.17 | 0.62 | Poor |
| Standardized vs individually tailored | 196 | 10 | 0.20 | 0.04 | 0.071 | 4.6** | 0.17 | 0.63 | Mixed |
| Targeted | 174 | 32 | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.046 | 0.1 | 0.17 | 0.64 | … |
| Train-the-trainer approach | 173 | 33 | 0.21 | 0.09 | 0.045 | 6.9*** | 0.17 | 0.63 | Good |
| Any behavioral intervention | 65 | 141 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.038 | 0.1 | 0.17 | 0.62 | Excellent |
| Behavioral interventions only | 151 | 55 | 0.17 | 0.25 | 0.043 | 4.0** | 0.17 | 0.63 | Mixed |
| Behavioral only vs behavioral with cognitive | 86 | 55 | 0.16 | 0.25 | 0.045 | 4.3** | 0.16 | 0.53 | … |
| Any cognitive intervention | 100 | 106 | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.036 | 2.5 | 0.17 | 0.63 | … |
| Cognitive interventions only | 186 | 20 | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.059 | 0.1 | 0.17 | 0.64 | … |
| Cognitive only vs cognitive with behavioral | 86 | 20 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.057 | 0.0 | 0.15 | 0.53 | Mixed |
| Multiple behaviors vs physical activity as only target | 115 | 87 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.037 | 1.0 | 0.17 | 0.63 | … |
| Individual vs group social context | 84 | 122 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.037 | 1.7 | 0.17 | 0.62 | … |
| Targeting individuals vs communities | 194 | 12 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0.057 | 3.2* | 0.16 | 0.58 | Good |
| Mediated delivery (e.g., telephone) | 71 | 135 | 0.29 | 0.15 | 0.041 | 11.7† | 0.16 | 0.61 | Poor |
| Work site program | 157 | 49 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.043 | 0.8 | 0.17 | 0.63 | … |
| Linked to primary care | 173 | 33 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.048 | 0.3 | 0.17 | 0.64 | … |
| Recommend specific physical activity | 121 | 85 | 0.18 | 0.20 | 0.037 | 0.4 | 0.17 | 0.63 | … |
| Recommend walking for physical activity | 148 | 38 | 0.17 | 0.23 | 0.048 | 1.2 | 0.18 | 0.66 | … |
| Recommend physical activity intensity | 15 | 49 | 0.22 | 0.18 | 0.076 | 0.2 | 0.17 | 0.61 | … |
Note. I2 = quantification of impact of heterogeneity; k0 = number of effect-size estimates with the moderator variable absent; k1 = number of effect-size estimates with the moderator variable present; 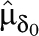 = mean effect size for studies without intervention component;
= mean effect size for studies without intervention component;  = mean effect size for studies with intervention component present; QB = between-groups heterogeneity statistic (distributed as χ2 on df = 1 under H0: μδ0 = μδ1);
= mean effect size for studies with intervention component present; QB = between-groups heterogeneity statistic (distributed as χ2 on df = 1 under H0: μδ0 = μδ1); 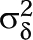 = residual between-studies variance component. Analysis reported if k0 ≥ 3 and k1 ≥ 3. Robustness assessed in joint moderator analyses. Ellipses indicate that no analyses were available for these rows.
= residual between-studies variance component. Analysis reported if k0 ≥ 3 and k1 ≥ 3. Robustness assessed in joint moderator analyses. Ellipses indicate that no analyses were available for these rows.
For all tabled moderators a test of H0: 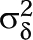 = 0 yielded P < .001.
= 0 yielded P < .001.
Excludes comparisons on the basis of fitness measures (≥ 6 months after supervised physical activity treated as physical activity behavior outcome).
*P < .10; **P < .05; ***P < .01; †P < .001, for QB.
