Figure 8.
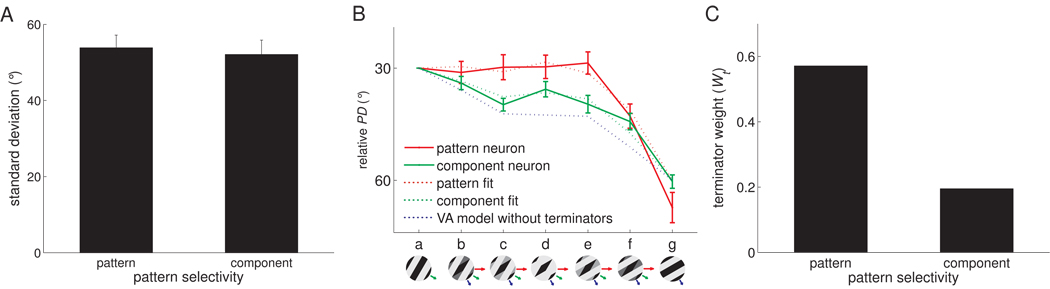
Comparing the properties of pattern and component neurons. A. Tuning width (circular standard deviation) of component and pattern neurons. The direction tuning of pattern neurons was not significantly wider than that of component neurons (t(40) = 0.24, p = 0.73). We used the median of the plaidness index (PI = Zp-Zc, see Figure 2) to discriminate pattern from component neurons. B. Mean of relative PD obtained from the responses to −30°/−60° type 2 plaids of pattern (red, N=13) and component (green, N=13) neurons, respectively, along with their corresponding VA predictions and predictions derived from a VA model without terminators. C. Pattern neurons receive stronger terminator signals, as evidenced by a higher terminator weight (Wt) compared to their component counterparts.