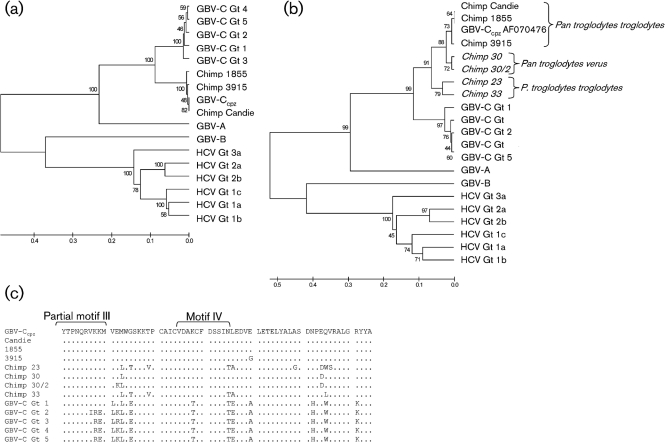
Fig. 5.
Phylogenetic relationships of RdRp of GB viruses and hepaciviruses. (a) RdRp amino acid sequences from GBV-Ccpz, GBV-C, HCV, GBV-A and GBV-B, and chimpanzees 1855 (HM626494), 3915 (HM626492) and Candie (HM626493) were aligned with clustal w. There are 231 aa in the final dataset. (b) GBV-Ccpz RdRp sequences from non-captive chimpanzees (noted in italics; see text) were included in the comparison. There are 61 aa in the final dataset. The evolutionary distances were computed using the Poisson correction method. Bootstrap values are shown for each branch point. Scales in (a) and (b) indicate the number of amino acid substitutions per site. (c) NS5B functional motifs III and IV are marked as described by Koonin (1991) from the NS5B alignment in (b).