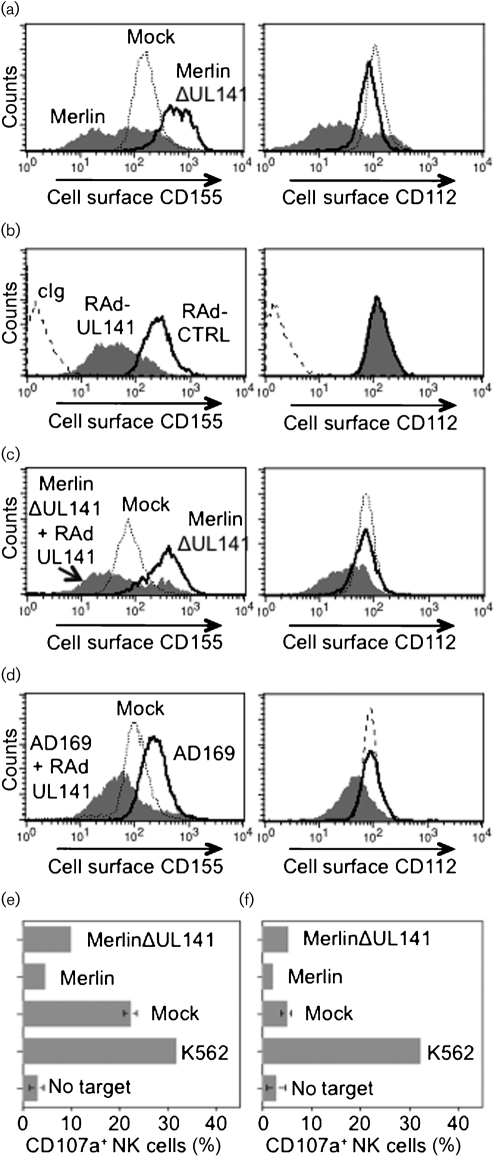
Fig. 3.
HFFF were infected for 72 h (m.o.i.=25) with HCMV strain Merlin or MerlinΔUL141, as indicated, and analysed for cell surface expression of CD155 and CD112 by flow cytometry. (b) HFFF were infected for 72 h (m.o.i.=200) with replication-deficient adenovirus vectors encoding HCMV UL141 (RAd-UL141) or equivalent empty RAd (RAd-CTRL) (Tomasec et al., 2005), as indicated, and analysed for cell surface expression of CD155 and CD112 by flow cytometry. (c) HFFF were co-infected for 72 h with MerlinΔUL141+RAd-CTRL or MerlinΔUL141+RAd-UL141, as indicated, and analysed for cell surface expression of CD155 and CD112 by flow cytometry. (d) HFFF were co-infected for 72 h with HCMV strain AD169+RAd-CTRL (AD169) or AD169+RAd-UL141, as indicated, and analysed for cell surface expression of CD155 and CD112 by flow cytometry. Control Ig histograms (cIg) were not included in panels (a), (c) and (d) to maintain figure clarity. (e) HFFF were infected for 72 h with HCMV strain Merlin, MerlinΔUL141 or mock infected. Sensitivity to NK cells was measured using alpha interferon (IFN-α) activated PBMC in allogeneic CD107a mobilization assay (Prod'homme et al., 2007) using the following antibodies: anti-CD107a-FITC (553793; BD Biosciences), anti-CD3-PerCP (SK7; BD Biosciences), anti-CD56-APC (N901; Beckman Coulter). PBMC incubated without targets and K562 cells are shown as controls. (f) RS primary skin fibroblasts were infected for 72 h with HCMV strain Merlin, MerlinΔUL141 or mock infected. Sensitivity to NK cells was measured using IFN-α activated RS PBMC in autologous CD107a mobilization assay as described in (e).