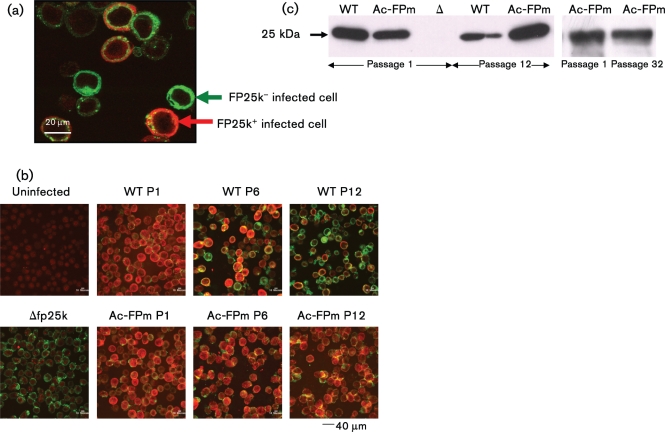
Fig. 3.
Modification of the fp25k gene by removal of TTAA sites leads to a larger fraction of cells with FP25K synthesis at later passages. (a) Sf-21 cells infected with WT AcMNPV or Ac-FPm at 48 h p.i. were stained for GP64 (green) and FP25K (red) protein to identify the FP25K-positive infected cells. (b) Comparison of the fraction of cells producing FP25K protein infected by WT AcMNPV or Ac-FPm at passages (P) 1, 6 and 12. Uninfected cells (no colour) and cells infected with Δfp25k AcMNPV (green only) were used as controls. The difference between WT AcMNPV- and Ac-FPm-infected cells producing FP25K protein at passage 12 was statistically significant (P<0.05, Student's t-test, n=3 fields of view). (c) Western blot analysis of FP25K protein synthesis at passages 1, 12 and 32 of WT AcMNPV and Ac-FPm viruses at 48 h p.i. Δ, Δfp25k AcMNPV.