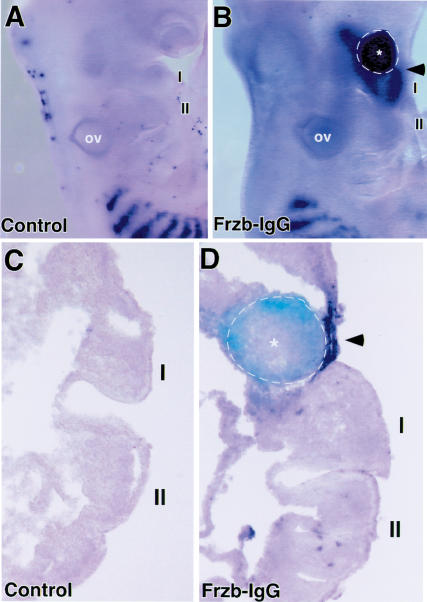
Figure 6.
Ectopic application of the Wnt antagonist Frzb induces MyoD expression in vivo. (A) Lateral view of the BA region of a control embryo and (B) an embryo in which a pellet of 293 cells, programmed to express Frzb-IgG, was inserted into the cranial paraxial mesoderm on the right side at stage 9. After 2 d of reincubation, the embryo was harvested and MyoD expression was analyzed by whole-mount in situ hybridization. Following in situ hybridization, the embryos were immunostained with an antibody against IgG to identify the location of the Frzb-IgG-expressing cells (indicated by dotted line). The BA containing the Frzb-IgG cells shows robust levels of MyoD expression (B). (C,D) Frontal sections through the BAs of the embryos displayed in A and B. Arrowhead in D points to location of ectopic MyoD expression in the BA mesenchyme located adjacent to Frzb-IgG cells (indicated by dotted line). For controls, we used staged-matched embryos that were mock-operated in the same manner and incubated for the same time period (A,C). Other controls included implantation of pellets of either 293 cells, 293-IgG cells, COS7 cells, or CHO cells into the cranial paraxial mesoderm on the right side of a stage 9 chick embryo, which in all cases failed to induce MyoD expression in the BAs (data not shown).