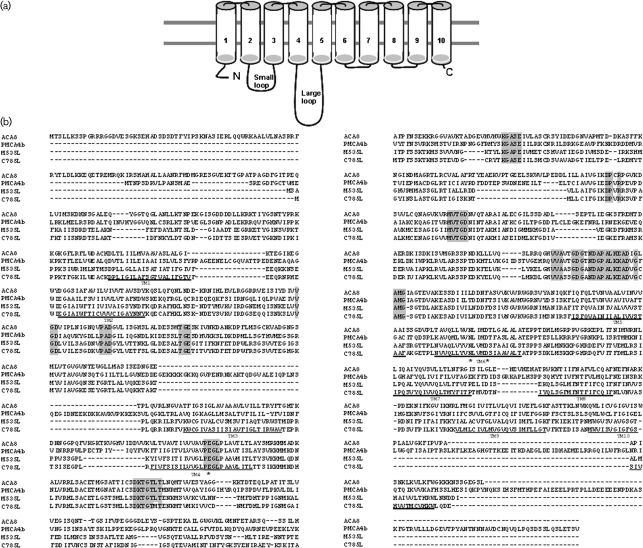
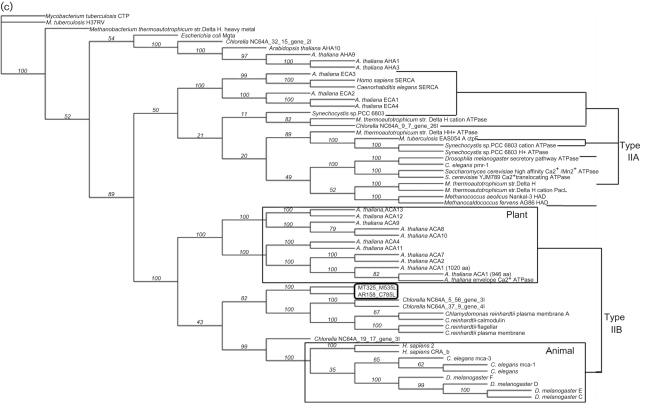
Fig. 1.
Predicted membrane topology, comparative alignment and phylogeny of chlorella virus Ca2+-transporting ATPases. (a) Hypothetical membrane topology of the viral Ca2+ pump. (b) Multiple sequence alignments performed with clustal w (1.82) of the deduced amino acid sequences of chlorella virus MT325 ORF M535L (NCBI reference no. ABT14089.1), chlorella virus AR181 ORF C785L (NCBI reference no. YP_001498866.1), and ACA8 (NCBI reference no. NP_200521.3) and PMCA4b (GenBank accession no. NM_001684) from A. thaliana and H. sapiens, respectively. Conserved residues characteristic for P-type ATPases type II are highlighted in grey. Residues corresponding to the single binding site for calcium found in type IIB Ca2+-ATPases are highlighted with asterisks. Bold lines indicate the ten transmembrane helices, TM1–TM10, predicted by the tmhmm program (www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM/). (c) Maximum-likelihood tree of 60 P-type ATPase protein sequences. The phylogenetic tree was generated using the muscle alignment and phyml tree building programs within the Geneious Pro 4.7.5 software program. The Whelan and Goldman (WAG) amino acid substitution model was used to derive 100 bootstrap datasets (the transition/transversion ratio for DNA models and the gamma distribution parameter were estimated, proportion of invariable sites was zero and four substitution rate categories produced the illustrated unrooted tree; bootstrap values are shown).