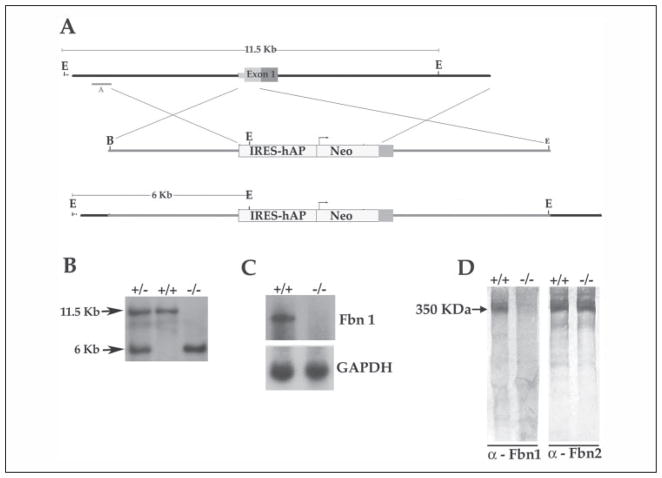
FIGURE 1. Fbn1 gene targeting strategy.
A, top to bottom, the wild-type genomic region that was targeted with the size of the wild-type EcoRI restriction fragment detected by probe A in the Southern analysis, the targeting vector containing the human alkaline phosphatase (hAP) and the phosphoglycerate kinase -neo (Neo) selectable gene with the arrow indicating the direction of transcription, and the targeted mgN allele with the size of the mutant EcoRI fragment detected by probe A. IRES, internal ribosome entry site. kb, kilo-bases. B, Southern blots of tail DNA from wild-type (+/+), heterozygous (+/−), and homozygous (−/−) mgN mice that was digested with EcoRI and hybridized to probe A; the size of DNA fragments (in kilobases) is indicated on the left side of the autoradiogram. C, Northern blots of RNA from lung tissues of wild-type (+/+) and mgN/mgN (−/−) mice hybridized to Fbn1 and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) probes. D, Western blots of conditioned media from wild-type (+/+) and mgN/mgN (−/−) mouse embryonic fibroblast cultures using anti-fibrillin-1 or fibrillin-2 antibodies (α); the size of fibrillins (in kDa) is indicated on the left side of the autoradiogram.