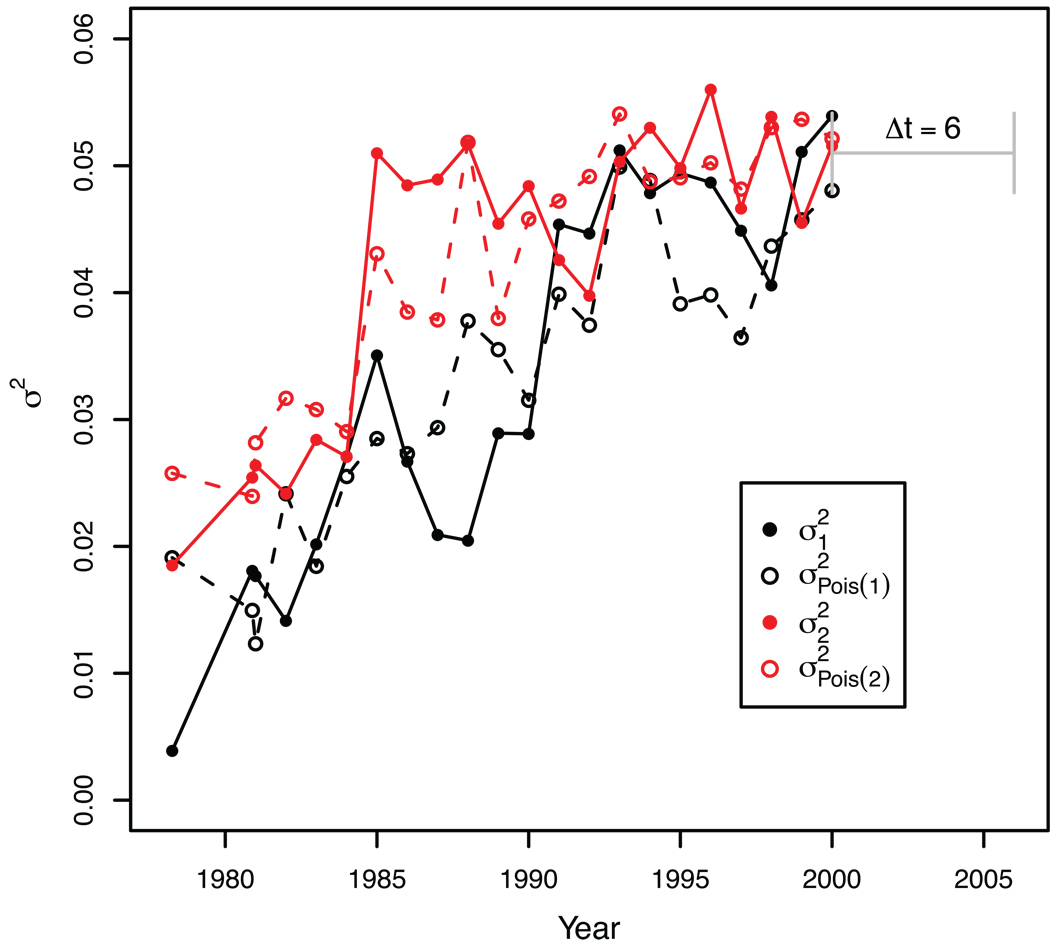
Figure 5. Comparison of HIV rate variance to Poisson variance.
The lines show the real variances σ12 (black) and σ22 (red) that our root optimization was based on compared to expected Poisson variances (σ2Pois(1) and σ2Pois(2), dashed lines) for the optimized real heights X̅1 and X̅2 of the HIV-1 subtype B data. Each data point indicates the tip height variance in a separate tree with Δt=6 years, plotted at time point 1. For simplicity, only the last time window is indicated in the graph (in grey). The expected Poisson variances were calculated from 1000 Monte Carlo simulated Xi ~ Pois(λ1=X̅1) and Xj ~ Pois(λ2=X̅2) per time window (44,000 simulated root-to-tip heights). The real variances were proportional to the expected Poisson variances (scale factors 75 and 79 for samples 1 and 2, respectively).