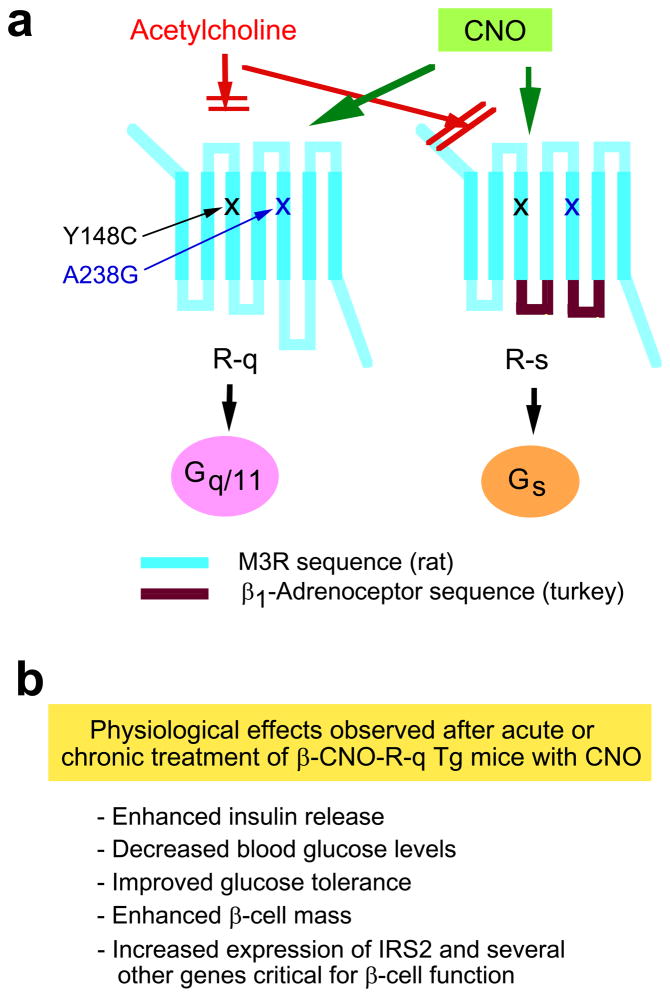
Figure 4.
Studies with clozapine-N-oxide (CNO)-responsive mutant M3Rs endowed with distinct G protein-coupling properties. (a) Structure of the M3R-based R-q and R-s designer receptors that can be selectively activated by CNO. The Y148C and A238G point mutations (rat M3R sequence) prevent acetylcholine binding to the M3R [35, 36]. Note that the Y148C and A238G point mutations (rat M3R sequence) correspond to the Y149C and A239G substitutions in the human M3R [35]. Both designer receptors can be efficiently activated by CNO, a pharmacologically inert compound. CNO binding to R-q leads to the selective activation of G proteins of the Gq/11 family [35, 36]. On the other hand, binding of CNO to R-s results in the selective activation of Gs [36]. (b) Phenotypic features of transgenic mice that express the R-q designer receptor selectively in pancreatic β-cells (β-CNO-R-q Tg mice). This short summary lists the key phenotypes that were observed after acute or chronic treatment of β-CNO-R-q Tg mice with CNO [36].