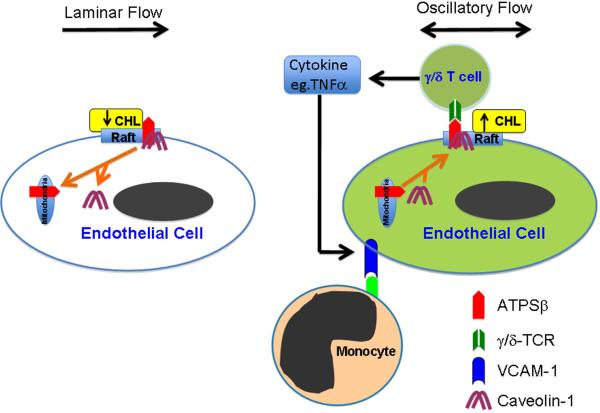
Figure 7. A proposed model of ATPSβ translocation in response to different flow patterns.
Laminar flow causes the translocation of ATPSβ/Cav-1 from membrane lipid rafts to mitochondria, which depends on membrane cholesterol level. Oscillatory flow increases membrane cholesterol, leading to ATPSβ translocation from mitochondria to membrane rafts, together with Cav-1. Oscillatory flow increases membrane ATPSβ, which can interact with TCR of γ/δ T cells, leading to the release of cytokines (e.g., TNFα) by the activated T cells. The secreted cytokines further enhance the VCAM-1 expression in ECs, which causes the adhesion of monocytes.