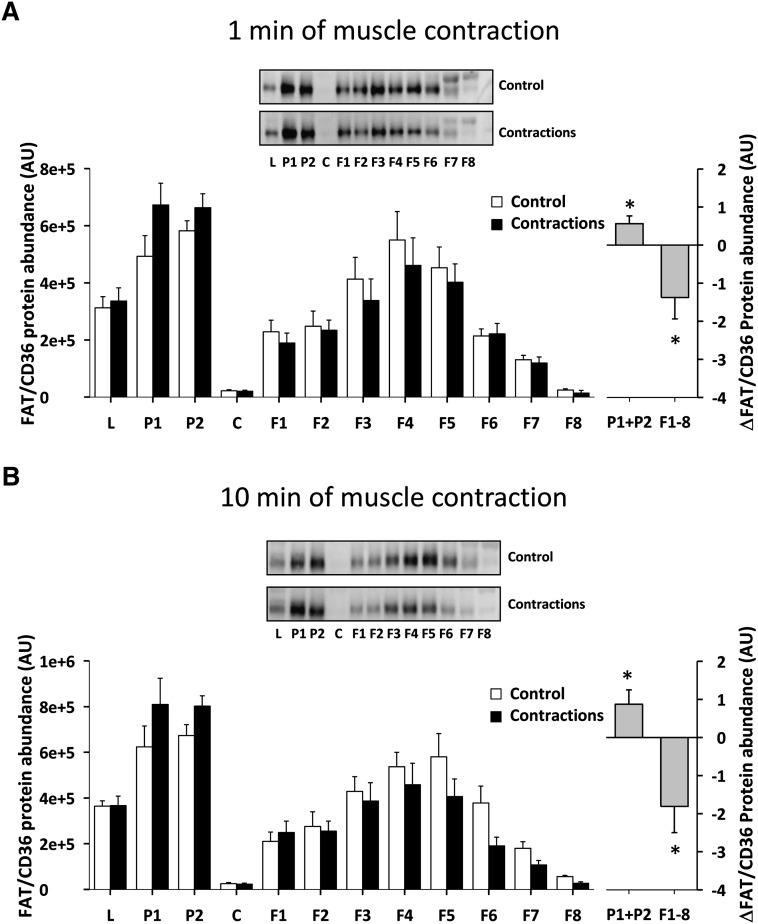
Fig. 6.
Skeletal muscle FAT/CD36 translocates rapidly in the perfused rat hindlimb muscle during contractions. Rats were anesthetized by an intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital sodium (4–5 mg/100 g body weight), and surgery for two-legged perfusion was performed. In one leg, isometric muscle contractions were induced in the gastrocnemius-plantaris muscle by stimulating the sciatic nerve electrically with supramaximal trains 5–15 V adjusted to obtain full fiber recruitment, 50 Hz with impulse duration of 1 ms, delivered every 3 s. Muscles were stimulated to contract for 1 or 10 min. There was a redistribution of FAT/CD36 to fractions enriched in heavy membranes away from low-density membranes after 1 min (A) (n = 6) and 10 min (B) (n = 6) of electrically induced muscle contraction compared with the resting contralateral control muscles. The left panels show the average data of each fraction and the right panels show the delta difference in abundance between conditions in surface membrane (P1+P2) and intracellular membranes (F1–F8). Data are means ± SEM, * significant difference from basal, P < 0.05. Representative images of immunoblots are shown. For statistical evaluation see Materials and Methods section.