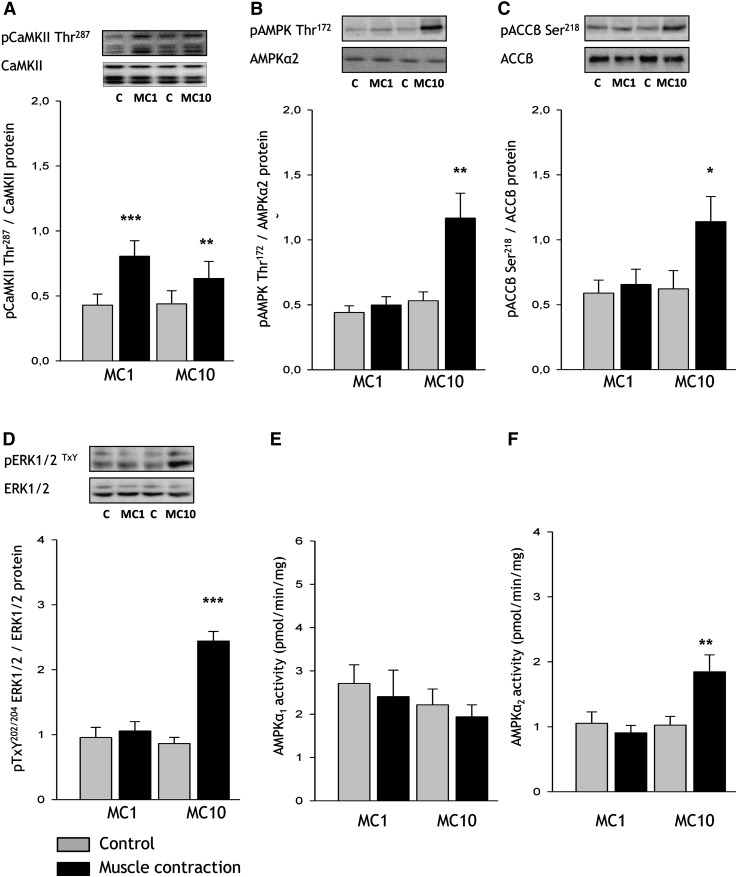
Fig. 7.
Skeletal muscle signaling with contraction stimuli in the perfused rat hindlimb. Rats were anesthetized by an intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital sodium (4–5 mg/100 g body weight), and surgery for two-legged perfusion was performed. Rats were subjected to sciatic nerve-induced contractions for either 1 (MC1) or 10 (MC10) min (n = 6) in situ, after which posterior hindlimb muscles (i.e., gastrocnemius and plantaris) from resting as well as stimulated conditions were excised. Phosphorylation of (A) calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKIIThr287), (B) AMP-dependent protein kinase (AMPK) Thr172, (C) acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) β Ser218, (D) extracellular-regulated protein kinase (ERK) TxY202/204, as well as AMPK α1 (E) and α2 activities (F) were determined in muscle lysates. Data are means ± SEM, */**/*** significant difference from basal, P < 0.05/0.01/0.001. Representative images of immunoblots are shown. MC, muscle contractions. For statistical evaluation, see Materials and Methods section.