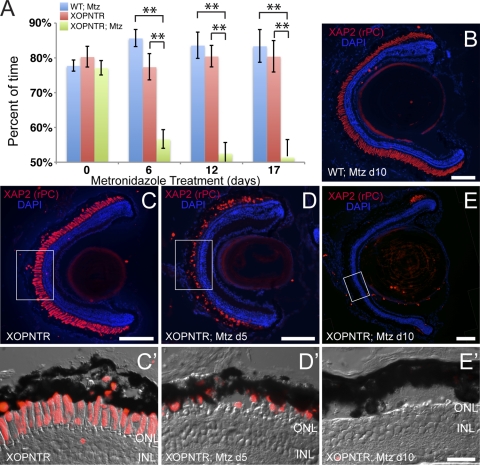
Figure 2.
Rapid vision loss and rod outer segment loss in Mtz-treated stage 50 XOPNTR tadpoles. (A) A behavioral assay was used to determine the effect of metronidazole on the dim-light vision of XOPNTR transgenic tadpoles and their wild-type (WT) siblings. Histogram bars indicate the average percentage of time spent on the white side of the test tank. Blue, red, and green bars denote wild-type Mtz-treated, XOPNTR DMSO-treated (referred to as untreated), and XOPNTR Mtz-treated tadpoles, respectively. The mean ± SEM is indicated. The behavioral responses of WT Mtz-treated and XOPNTR untreated animals were not statistically different at any time point, whereas the Mtz-treated animals were significantly different from both control groups on treatment days 6, 12, and 17. Immunohistochemistry was used to determine the effect of Mtz treatment on rod photoreceptors. Retinal sections were stained to detect rod photoreceptor outer segments (XAP2; red) and cell nuclei (DAPI; blue). Wild-type (B) and transgenic (C–E) tadpoles were treated for 5 days with DMSO only (C) or for 5 or 10 days with Mtz (B, D, E). Higher magnification views of the boxed regions in C–E are shown in C′–E′. Scale bars: 100 μm (B–E); 25 μm (C′–E′). **P ≤ 0.01.