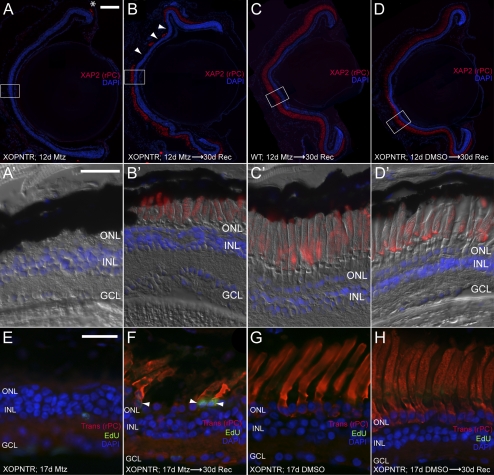
Figure 6.
Rod photoreceptor regeneration in XOPNTR tadpoles. Stage 53 tadpoles were cultured in Mtz for 12 days and processed immediately (A, A′) or were allowed to recover an additional 30 days (B–D′) before immunohistochemistry. Retinal sections were stained for XAP2 to detect outer segments of rod photoreceptors. In XOPNTR animals treated with Mtz for 12 days, rod outer segments were only detected in the most peripheral retina (A, asterisk). After a 30-day recovery, rod outer segments were again detected in the central retina (B, B′), but they were shorter than rods of wild-type Mtz-treated (C, C′) and XOPNTR untreated (D, D′) tadpoles. (A′–D′) Magnified views of the boxed regions in (A–D). (B, arrowheads) Regions lacking rod outer segments. Regenerated rods are EdU-positive. Mtz-treated (E, F) and untreated (G, H) stage 53 XOPNTR tadpoles were injected intra-abdominally with EdU, cultured for 17 days, and processed immediately (E, G) or allowed to recover in Mtz-free media for an additional 30 days (F, H) before immunohistochemistry. Retinal sections were stained to detect nuclei (DAPI; blue), rod photoreceptors (transducin; red), and cells that had passed through S-phase during treatment (EdU; green). Scale bars: 100 μm (A–D); 25 μm (A′–D′, E–H).