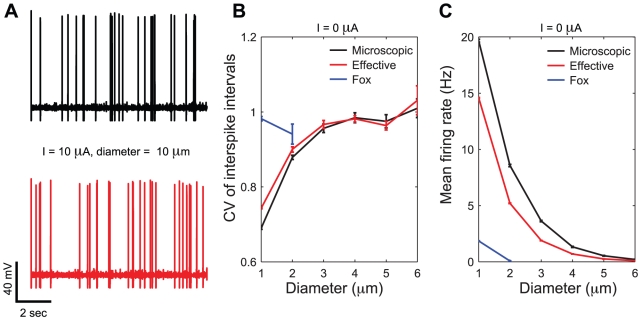
Figure 4. Spontaneous firing in the microscopic and effective models.
When weakly depolarising DC currents (A, 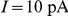 ) are applied to both the microscopic (black sample trace) and the effective models (red sample trace), the increase in channel noise variances (see Fig. 2C,F) induces a highly irregular spontaneous emission of action potentials, with qualitatively very similar properties. In these simulations, both length and diameter of the neuron are set to
) are applied to both the microscopic (black sample trace) and the effective models (red sample trace), the increase in channel noise variances (see Fig. 2C,F) induces a highly irregular spontaneous emission of action potentials, with qualitatively very similar properties. In these simulations, both length and diameter of the neuron are set to 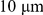 , and the single channel conductance for both sodium and potassium channels is
, and the single channel conductance for both sodium and potassium channels is 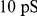 . Panels B,C show respectively the CV of the ISI distribution and the mean firing rate as a function of cell diameter: results are reported for the microscopic, effective and Fox's models (black, red and blue traces, respectively). The results of panels B,C refer to spontaneous activity (i.e., no injected current) with neuron length held fixed at the value
. Panels B,C show respectively the CV of the ISI distribution and the mean firing rate as a function of cell diameter: results are reported for the microscopic, effective and Fox's models (black, red and blue traces, respectively). The results of panels B,C refer to spontaneous activity (i.e., no injected current) with neuron length held fixed at the value 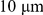 .
.