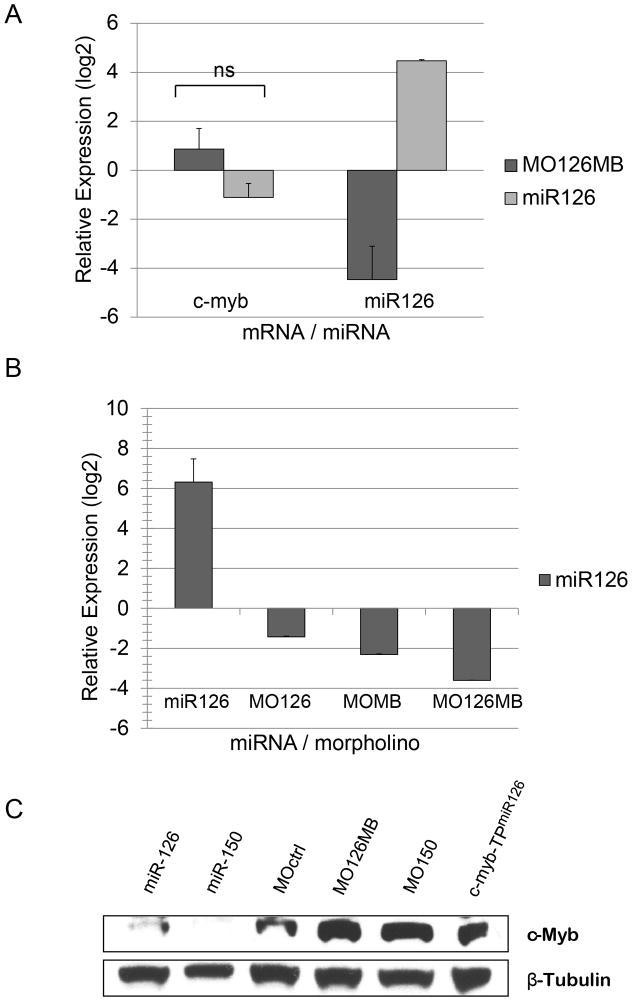
Figure 3. In vivo manipulation of miR-126 levels in zebrafish embryos and regulation of regulates c-Myb in zebrafish embryos and HSCs.
(A) Hematopoietic stem cells were isolated from a transgenic zebrafish line Tg(c-myb:EGFP) at 36 hpf and c-myb mRNA and miR-126 levels were analyzed by qRTPCR. Knockdown or enforced expression of miR-126 reduced or increased mature miR-126 levels in HSCs compared to control morpholino (MOctrl) injections and normalized to gapdh mRNA levels. Although c-myb mRNA levels mirrored miR-126 levels, the changes were not statistically significant. Average values of two independent experiments in triplicate are shown with the standard deviation of biological replicates indicated. Relative expression levels are depicted in logarithmic scale.
(B) miR-126 levels in zebrafish embryos at 24hpf were determined by qRTPCR normalized to control injections and zf-gapdh. Injection of miR-126 duplex (5μM) resulted in an almost 80-fold increase of mir-126 levels. Injection of a morpholino targeting the mature miR-126 (MO126, 2mM), or a multiblocker-morpholino targeting the Drosha and Dicer sites in the pre-miR-126 (MOMB, 0.8mM) or a combination of MO126 and MOMB (MO126MB) yielded a 2.6-fold, 4.9-fold or 12-fold reduction of mature miR-126 levels, respectively. Relative expression levels are depicted in logarithmic scale.
(C) Increased c-Myb protein levels are observed with the functional inhibition of miR-126 using a combination of MO126 and MOMB (MO126MB) or the target protector (c-myb-TPmiR126), and by the functional knockdown of miR-150. The enforced expression of miR-126 or miR-150 results in a marked reduction of c-Myb relative to MOctrl injections. β-Tubulin expression was used as a loading control.