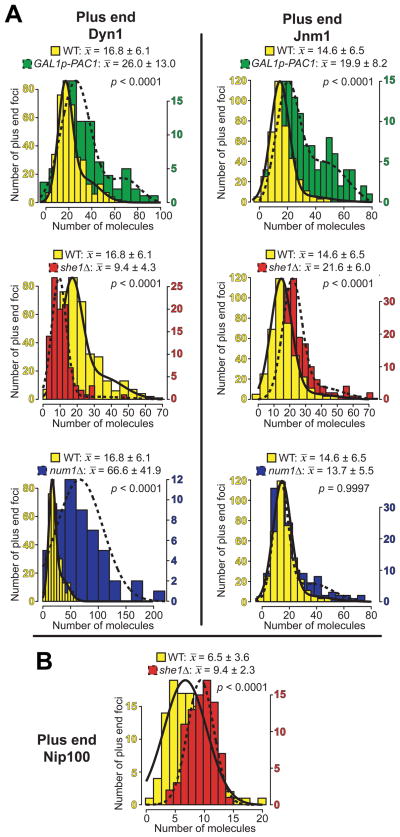
Figure 4. GAL1p-PAC1, she1Δ, and num1Δ differentially affect the recruitment of dynein and dynactin to the MT plus end.
Histograms of the number of molecules per plus end focus, shown together with Gaussian fits (see Materials and Methods and Supplementary Note 1), for (A) Dyn1 or Jnm1 in a wild-type (nDyn1 = 380 foci; nJnm1 = 385 foci), GAL1p-PAC1 strain (nDyn1 = 80 foci; nJnm1 = 124 foci), she1Δ (nDyn1 = 100 foci; nJnm1 = 170 foci), or num1Δ (nDyn1 = 52 foci; nJnm1 = 153 foci) strain, or (B) Nip100 in a wild-type or she1Δ strain (nSHE1 = 108 foci; nshe1Δ = 83 foci). Mean values for the first major component (i.e., x̄1 from Fig. S4) ± standard deviation are shown. P values between wild-type and mutant are indicated. For 2-component data sets, only those values probabilistically determined to occupy the first component were used to calculate P values.