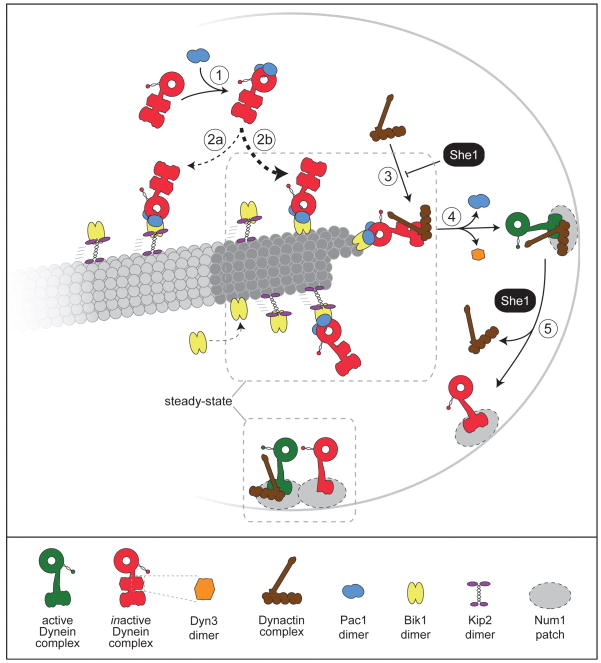
Figure 6. Schematic of the pathway for dynein and dynactin targeting to the plus end and cell cortex.
Our data indicate that the dynein complex associates with cytoplasmic Pac1 in a 1:1 ratio (step 1) prior to interacting with plus end-bound Bik1 (step 2). Previous studies have established that Bik1/CLIP-170 is targeted to the plus end either by direct recruitment from the cytoplasm (Bieling et al. 2008; Dixit et al. 2009; Dragestein et al. 2008; Folker et al. 2005) or via a Kip2 kinesin-dependent mechanism (Carvalho et al. 2004). Our previous data (Markus et al. 2009) showed that dynein plus end targeting is predominantly independent of Kip2 (reflected by the thickness of the dashed arrows for step 2a versus 2b). A previous study in budding yeast demonstrated that dynein then recruits dynactin to the plus end (Moore et al. 2008). Our data here indicate that only 1 dynactin complex is recruited for every 3 plus end dynein complexes. Association of dynein with dynactin (step 3), which is negatively regulated by She1 (Woodruff et al. 2009) (Fig. 4; Table 3), is a requisite for the offloading of dynein-dynactin to Num1 patches at the cell cortex (step 4) (Lee et al. 2003; Moore et al. 2008; Sheeman et al. 2003). Each cortical Num1 patch consists of ~14 molecules of Num1 (Tang et al. 2009) (not all molecules are drawn). Since Pac1 and Dyn3 are not found at the cell cortex, they likely dissociate from the dynein complex during step 4 (Lee et al. 2005; Lee et al. 2003). Based on our observations in this study, we propose that She1 mediates the dissociation of dynactin from cortically anchored dynein (step 5) (see Discussion), thus maintaining a steady-state ratio of 1 dynactin per 2 dynein complexes. Our data indicate that assembled cortical dynein-dynactin complexes (green) are active, while cortical dynein without dynactin is inactive (red). Dashed gray boxes outline a diagrammatic summary of the stoichiometry our counting data has revealed for MT plus ends and the cell cortex. See Figure S4 regarding plus end Dyn3 and Figure S5 regarding cortical Pac11.