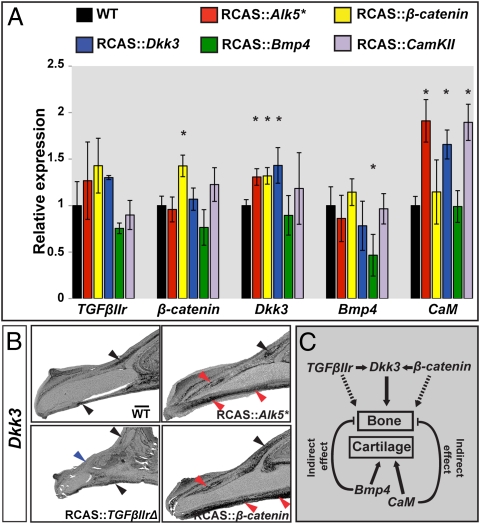
Fig. 4.
Interaction of genes regulating beak development. (A) Quantitative real-time PCR assays measuring gene expression levels of TGFβIIr, β-catenin, Dkk3, Bmp4, and CaM in embryos infected with RCAS constructs. Expression levels are shown relative to wild-type uninfected controls (asterisks denote significance at P < 0.05, t test, n = 5; error bars represent SD values). Up-regulation of the TGFβ pathway and of β-catenin led to higher expression of Dkk3 (A and B). Conversely, down-regulation of the TGFβ pathway caused a decrease Dkk3 expression (B). Blue arrows indicate lower expression relative to wild-type specimens, red arrows indicate higher expression, and black arrows indicate no change (see text for details). (Scale bar, 0.4 mm.) (C) A general model of beak development in which Bmp4 and CaM act independently to alter the growth of the prenasal cartilage and TGFβIIr, β-catenin, and Dkk3 regulate the premaxillary bone.