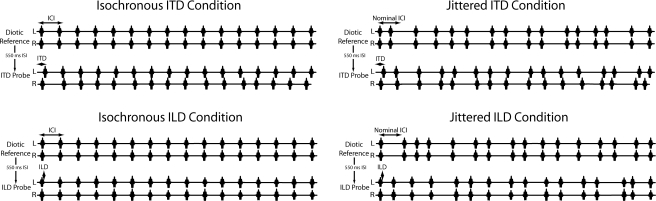
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of stimuli (not to scale). Each trial consisted of a diotic reference stimulus followed by a probe stimulus. In isochronous (left) conditions (tested in a previous investigation), the reference stimulus was comprised of 16 equal-amplitude Gabor clicks presented synchronously to the left and right earphones. Following a 550 ms silent interval, an ITD or ILD probe stimulus was presented, comprised of 16 Gabor click pairs with random ITD or ILD imposed on each. In the ITD probe, each click pair carried an ITD drawn from a uniform distribution of ±100 μs about a base ITD of −100, 0, or 100 μs (0 in the above illustration); clicks were presented at equal amplitude to the two earphones in this condition. In the ILD probe, each click pair carried an ILD drawn from a uniform distribution of ±2 dB about a base ILD of −1, 0, or 1 dB (0 in the above illustration); clicks were presented synchronously to the two earphones in this condition. The ICI, which corresponded to the rate of click presentation, was held constant within and between trials of a single run. The jittered conditions (right) were identical to the isochronous conditions with the exception that the ICI in both the reference and probe stimuli were varied randomly about the nominal ICI according to the parameter k (see text).