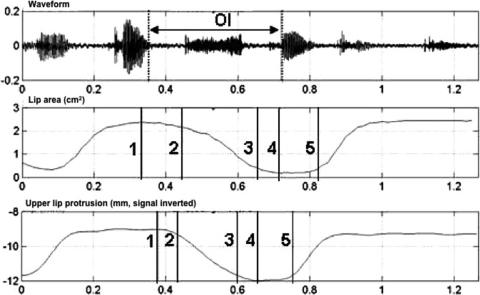
Figure 3.
Above: the waveform time (s); center: lip area time course (cm2); below: upper-lip protrusion time course (mm; inverted for visual correspondence with constriction) for a sequence [iksku] in the sentence “Deux kixes coukiquent” uttered by a Canadian French speaker in the BB condition. The OI is determined on the spectrogram by the acoustic offset of [i] and the acoustic onset of [u] formants. Identification of events on the lip area time course: 1 = maximal area for [i]; 2 = 10% of area difference between [i] and [u]; 3 = 90% of area range between [i] and [u]; 4 = minimal area for [u]; 5 = 10% of lip area difference between [i], and [u] following minimal area of [u]. Interval 2–3 corresponds to TF and interval 3–5 to the duration of the H phase. Identification of events on the upper-lip protrusion time course: 1 = minimal protrusion for [i]; 2 = 10% of protrusion difference between [i] and [u]; 3 = 90% of protrusion range between [i] and [u] ; 4 = maximal protrusion for [u]; 5 = 10% of protrusion difference between [i] and [u] following maximal protrusion of vowel [u]. Interval 2–3 also corresponds conventionally to the duration of protrusion TF and interval 3–5 to protrusion H.