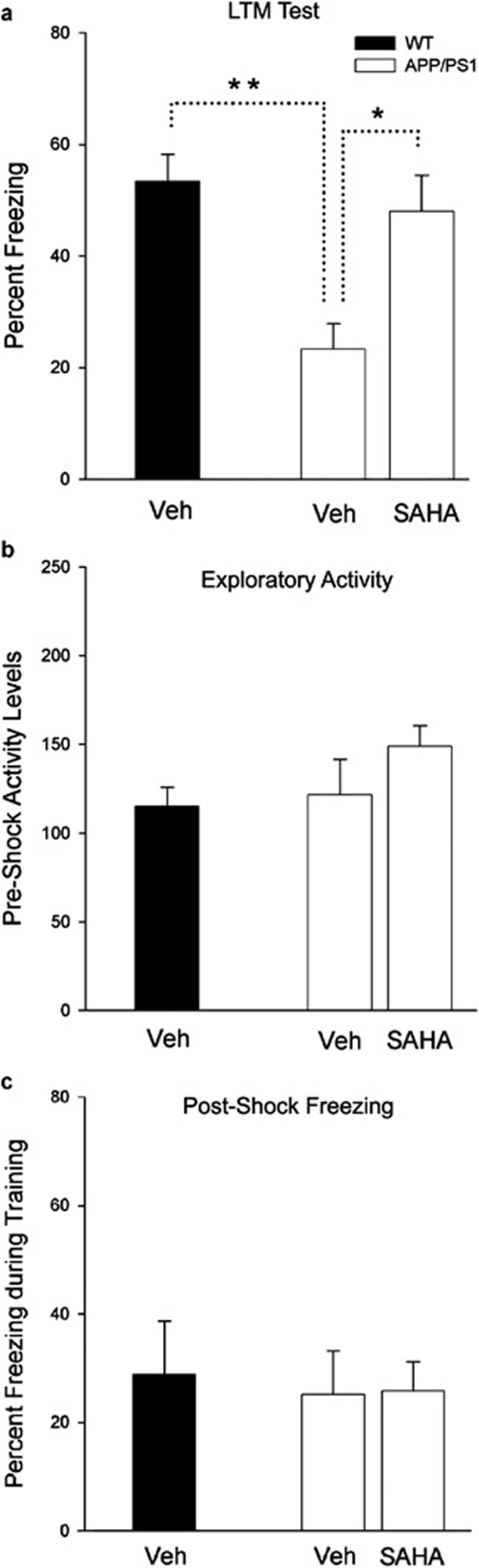
Figure 3.
Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) rescues memory deficits in APPswe/PS1dE9 mice. (a) Wild-type (WT) and APP/PS1 (6-month-old) mice were injected with either vehicle (VEH) or 50 mg/kg SAHA daily for 19 days (VEH: WT n=7, APP/PS1 n=7; NaB: APP/PS1 n=7). All mice were then trained in a contextual fear conditioning paradigm and tested for long-term memory 24 h later. Freezing was measured for each animal. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) tests were performed, F(2,20)=8.93, P<0.005. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. (b) Exploratory activity was measured for each animal during 150 s period before the footshock (F(2,18)=0.06, P>0.05). (c) Percent freezing was calculated for each animal during the 28 s period immediately after the footshock (F(2,18)=1.50, P>0.05).