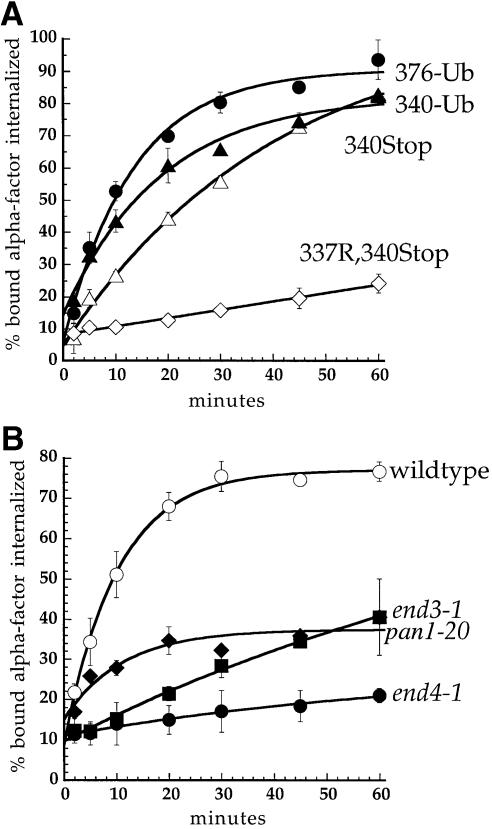
Fig. 2. Ubiquitin fused in-frame to Ste2p at amino acids 340 or 376 directs internalization of Ste2p–Ub chimeric proteins. All curves represent the average of at least three independent experiments and error bars depict the standard deviation. (A) Ste2p and Ste2p–Ub variants were introduced into ste2Δ cells and the resulting strains were assayed for their ability to internalize 35S-labeled pheromone. Cells were harvested and incubated with [35S]α–factor at 4°C, unbound α–factor was removed, and casamino acid medium pre-warmed to 30°C was added to initiate internalization. At various times aliquots of the cells were removed and the ratio of internal to total cell-associated α–factor was measured. Internalization half-times were determined by a simple exponential curve fit using Kaleidagraph software. Ste2p- 376–Ub (LHY558, •; t1/2 = 9.2 min); Ste2p-340–Ub (LHY844, ▴; t1/2 = 12.8 min); Ste2p-340Stop (LHY847, ▵; t1/2 = 28.3 min); Ste2p-337R,340Stop (LHY319, ⋄; t1/2 >200 min). (B) Wild-type (LHY558, ○), end3-1 (LHY1488, ▪), end4-1 (LHY1490, •) or pan1-20 (LHY1580, ♦) strains expressing Ste2p-376–Ub (LHP361) as their sole source of Ste2p were propagated in casamino acid medium and shifted to the non-permissive temperature of 37°C for 20 min. 35S–labeled α–factor was added and the ratio of internalized to total cell-associated α–factor was determined at different time points.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.