Figure 1. Characteristics of the excitatory axo-axonic connection between the Mauthner (M-) and cranial relay neuron (CRN) axons.
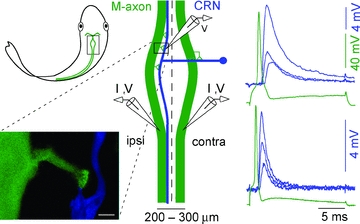
Location of M-axon–CRN connection in goldfish hindbrain is highlighted with a rectangle (upper left). For clarity only one CRN is illustrated and as indicated, a CRN receives input from both M-axons. Expanded diagram (centre) depicts the typical contact locations (triangles) between a presynaptic M-axon (green) and a postsynaptic CRN axon (blue). M-axons 50–100 μm in diameter run within 75–400 μm of each other and parallel to the midline (dashed line). The lower left panel shows a confocal image of a M-axon (green)–CRN (blue) axo-axonic contact. The calibration bar is 20 μm. Right, current pulses (I) injected into either the ipsilateral or contralateral M-axon generate a presynaptc action potential followed by EPSPs that depress with increasing stimulus number (1, 2 and 10) at 1 Hz. The EPSP decay kinetics differ among CRNs and can range from slow (upper right) to fast (lower right).
