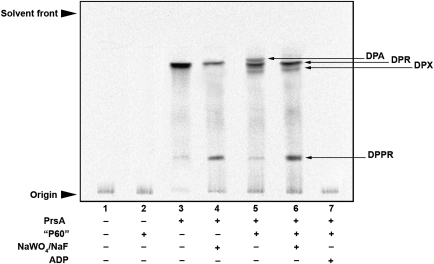
Fig. 3.
Analysis of Mt-PrsA-dependent [14C]-R5P incorporation into the M. smegmatis AraT substrate DPA via p[14C]Rpp. The basic assays mixture contained (amongst other components described in the Materials and methods section) membranes prepared from M. smegmatis, 100,000 cpm [14C]-R5P, 50 µg of DP and 2 mM ATP. Individual assays were carried out at 37°C and included the addition of no further additive; lane 1, M. smegmatis P60; lane 2, Mt-PrsA; lane 3, Mt-PrsA and NaWO4 and NaF both at a final concentration of 2 mM; lane 4, Mt-PrsA and M. smegmatis P60; lane 5, Mt-PrsA, M. smegmatis P60 and 2 mM of both NaWO4 and NaF; lane 6 and finally Mt-PrsA, M. smegmatis P60 and 2 mM ADP in lane 7. After an incubation at 37°C for 30 min, assays were quenched and products extracted from the assay mix by organic solvent extraction as described in the Materials and methods section. Samples relating to each assay were loaded onto a silica gel TLC plates, developed in CHCl3/CH3OH/CH3COONH4/NH4OH/H2O (180:140:9:9:23 v/v/v/v/v) and bands migrating to the position of DPA, DPR, DPX and DPPR were visualized by autoradiography, exposure of TLCs to X-ray film (Kodak X-Omat) and compared to previously isolated known standards (Mikusova et al. 2005; Alderwick et al. 2006a).