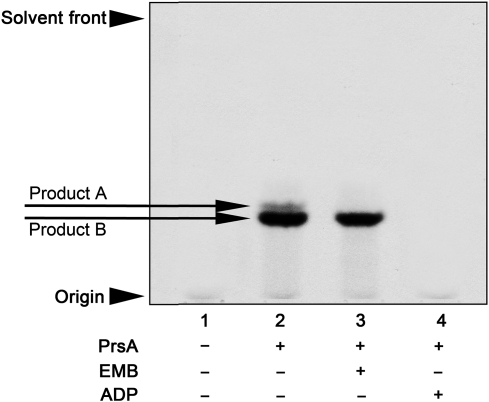
Fig. 4.
AraT assays carried out via the Mt-PrsA-dependent conversion of [14C]-R5P to p[14C]Rpp and subsequent chase into a neoglycolipid acceptor. The absolute dependence of the cell wall AraT enzymes on the availability of pRpp was investigated using the neoglycolipid acceptor Ara2. The basic assay contained (amongst other components described in the Materials and methods section) 0.5 mg of membranes and P60 from M. smegmatis, 2 mM α-d-Araf-(1 → 5)-α-d-Araf-O-(CH2)7CH3, 100,000 cpm [14C]-R5P, 50 µg of DP and 2 mM ATP. Assays were initiated by the addition of [14C]-R5P and incubated for 1 h at 37°C. Individual assays carried out contained the addition of no Mt-PrsA, lane 1; 30 µg of Mt-PrsA, lane 2; 30 µg of Mt-PrsA and 100 µg/mL of EMB, lane 3 and 30 µg of Mt-PrsA and 2 mM ADP, lane 4. [14C]-Araf-linked products were extracted from the assay mix as described in the Materials and methods section and subsequently applied to a silica gel TLC plates, developed in CHCl3:CH2OH:H2O:NH4OH (65:25:3.6:0.5, v/v/v/v) and visualized by autoradiography from exposure of TLCs to X-ray film (Kodak X-Omat; Lee et al. 1997; Seidel et al. 2007).