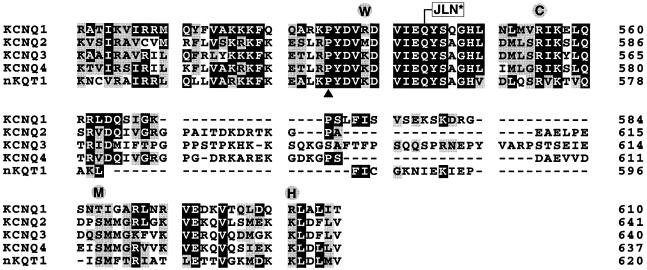
Fig. 2. Alignment of C–terminal sequences conserved in the KCNQ family. KCNQ1 encoding the KvLQT1 protein (Chouabe et al., 1997; Yang et al., 1997), KCNQ2 (Biervert et al., 1998; Singh et al., 1998), KCNQ3 (Charlier et al., 1998), KCNQ4 (Kubisch et al., 1999) and nKQT1 (Wei et al., 1996) sequences were aligned using the clustalw algorithm of the Meglign (DNAstar Inc.) program. Numbers on the right side refer to the last amino acid residue in each lane. Residues that are identical in at least three out of the five sequences are boxed in black, structurally conserved residues are boxed in grey. KCNQ1 point mutations associated with the LQT syndrome (Chouabe et al., 1997; Itoh et al., 1998; Neyroud et al., 1999) are circled. The deletion–insertion mutation at the amino acid residue linked to JLN syndrome (Neyroud et al., 1997) is indicated by a boxed JLN*. An insertion mutation (▴) in the homologous region of KCNQ2 has been linked to the occurrence of benign familial neonatal convulsions (Biervert et al., 1998).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.