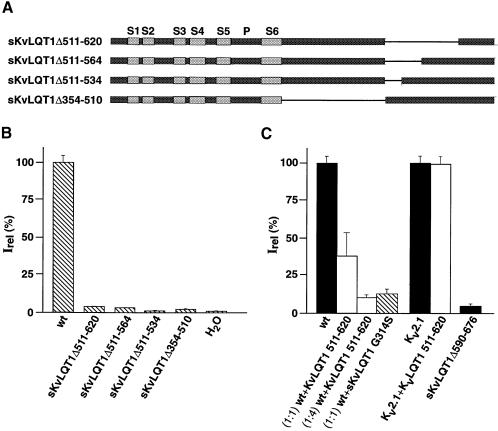
Fig. 3. Effect of internal deletions on expression of KvLQT1 currents. (A) Diagram illustrating sKvLQT1 constructs used for heterologous expression in Xenopus oocytes (B) and in CHO cells (C). Numbers in deletion constructs refer to amino acid residues of full-length KvLQT1 protein (see Figure 1). (B) Currents were measured after injection of cRNA encoding sKvLQT1, sKvLQT1Δ511–564, sKvLQT1Δ511–534 and sKvLQT1Δ354–510, respectively, and for control H2O. In each case, currents were evoked with voltage jumps to +40 mV from a holding potential of –80 mV. Data pooled from 4–20 oocytes. The 100% Irel value corresponds to the steady-state current amplitude of sKvLQT1, which was measured at +40 mV 4 s after voltage jump. (C) Currents were measured in transfected CHO cells in the whole-cell configuration of the patch–clamp technique. Cells were transfected with KvLQT1 DNA, sKvLQT1Δ590–676 DNA, Kv2.1 DNA (black bars) or mixtures of KvLQT1 DNA with KvLQT1 511–620 (white bars) or KvLQT1 G314S (hatched bar) as indicated under each column bar. For the control, CHO cells were transfected with a 1:1 mixture of Kv2.1 and KvLQT1 511–620 DNAs. Current amplitudes were measured after voltage jumps from –80 to +40 mV. Data were pooled from 4–16 cells. Current amplitudes were related to each other by setting wt KvLQT1 current amplitude (82 pA/pF) to 100% and Kv2.1 current amplitude (711 pA/pF) to 100%.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.