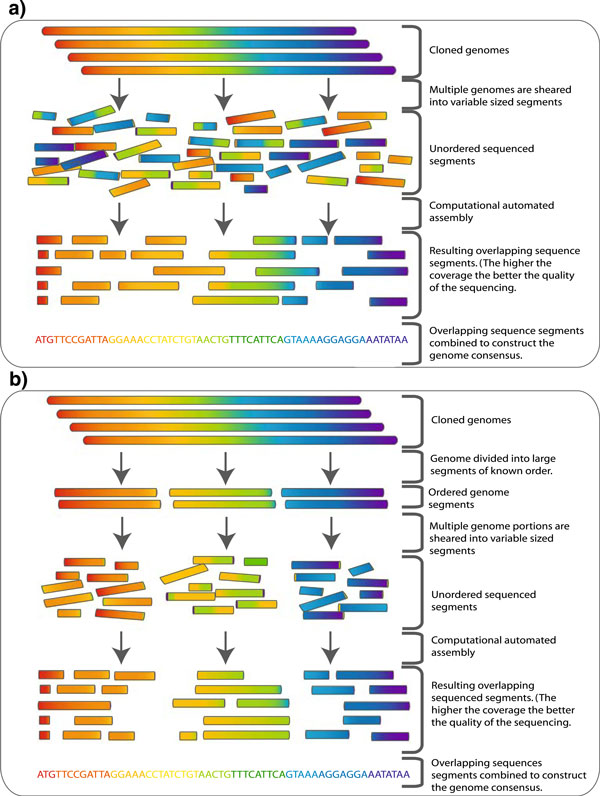
Figure 1.
a Whole genome shotgun sequencing: Genome is sheared into small approximately equal sized fragments which are subsequently small enough to be sequenced in both directions followed by cloning. The cloned sequences (reads) are then fed to an assembler (illustrated in Figure 2). b To overcome some of the complexity of normal shotgun sequencing of large sequences such as genomes a hierarchical approach can be taken. The genome is broken into a series of large equal segments of known order which are then subject to shotgun sequencing. The assembly process here is simpler and less computationally expensive.