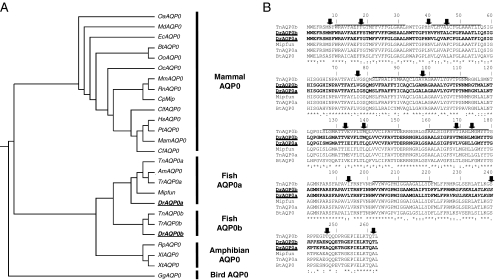
Figure 1.
Sequence comparisons of AQP0s. (A) Dendrogram of AQP0s, generated by CLUSTALW using AQP0 sequences. AQP0 sequences from fish are divided into two distinct branches, Aqp0a and Aqp0b. Species with the entire genome data are italicized (OaAQP0-Ornithorhynchus, MdAQP0-Opposum, EcAQP0-Horse, BtAQP0-Bovine, OoAQP0-Sheep, OcAQP0-Rabbit, MmAQP0-Mouse, RnAQP0-Rat, CpAQP0-Guinea Pig, CfAQP0-Dog, HsAQP0-Human, PtAQP0-Chimpanzee, MamAQP0-Macacca, CfAQP0-Cat, TnAQP0-Pufferfish, AmAQP0-Mexican tetra, TrAQP0-Pufferfish fugu, MIPfun-Killifish, DrAQP0-Zebrafish, RpAQP0-Frog, XlAQP0-Xenopus laevis, XtAQP0-Xenopus tropicalis, GgAQP0-Chicken). (B) Sequence alignment of AQP0s from zebrafish (DrAqp0a and DrAqp0b), tetraodron (TnAqp0a and TnAqp0b), killifish (MIPfun), and bovine (BtAQP0), generated by CLUSTALW. Solid lines: six predicted transmembrane regions of aquaporins. Amino acid identities between the sequences are indicated with asterisks, strong similarities are indicated with colons, and weak similarities are indicated with dots. Of the positions that distinguish the cluster of Aqp0a sequences from the cluster of Aqp0b sequences (black arrows), half are in transmembrane domains that face another monomer in either the tetramer or the lipids. For example, positions 18 and 139 in mammalian AQP0 face each other in the neighboring monomer in the tetramer, position 46 faces itself, and position 77 faces the lipids. Almost all differences are in the lengths of the amino acids side chains (variations of V, L, I, M). For 8 of 14 positions Aqp0bs have the same amino acid as mammalian AQP0; for 5 of 6 remaining positions, Aqp0as have the same amino acid as mammalian AQP0.