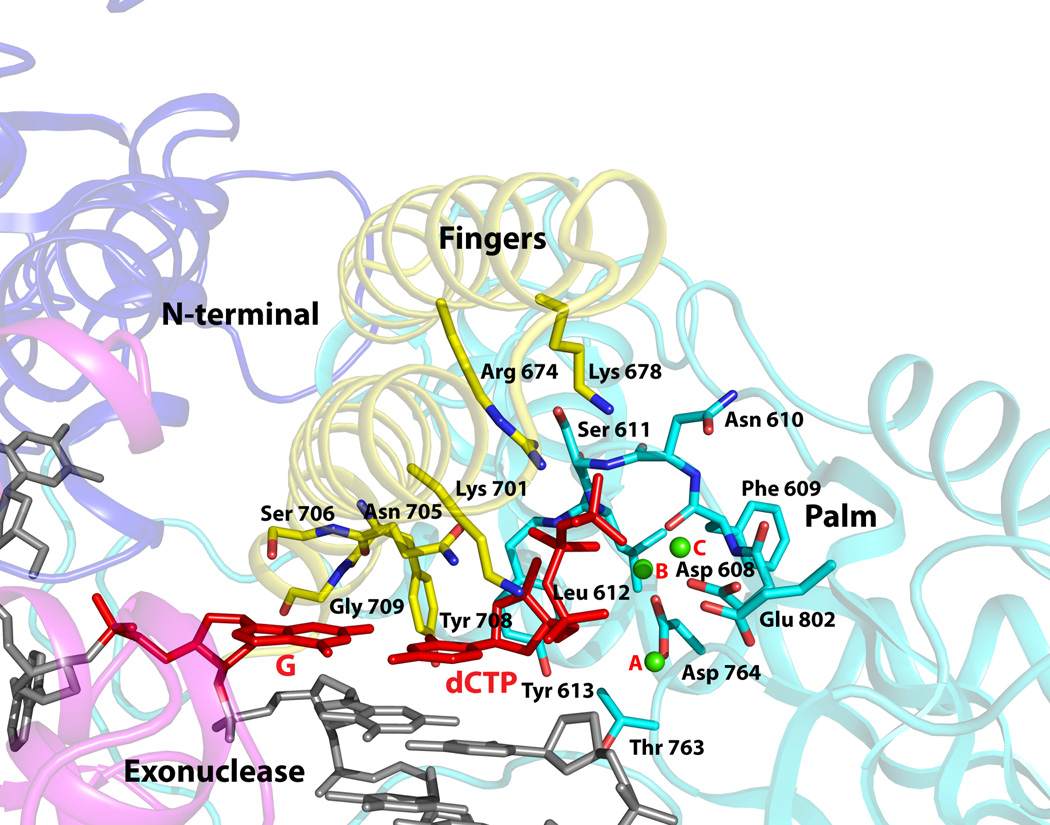
Figure 3. Close-up view of the polymerase active site region.
The fingers, palm, exonuclease, and the N-terminal domains are colored in faded yellow, cyan, magenta, and blue. The DNA is colored gray, templating G and incoming dCTP are in red, and the Ca2+ ions (A, B and C) are in green. Highlighted and labeled are the acidic residues (Asp608, Asp764 and Glu802); residues that interact with the triphosphate moiety of incoming dCTP via side chain (Arg674 and Lys701), main chain (Ser611 and Leu612), and a water molecule (Lys678); residues that impinge on the dG-dCTP bases (Asn705, Ser706, Tyr708, and Glu709); and Tyr613 that stacks against the dCTP sugar. The residues are colored to match the domain they belong to.