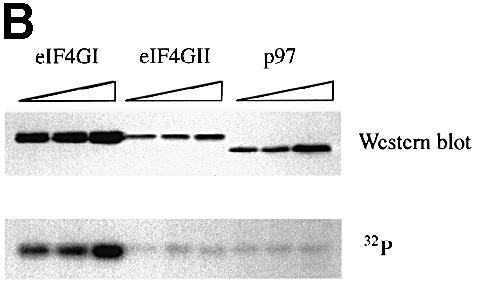
Fig. 3. The phospho-region of eIF4GI is poorly conserved within the human eIF4G family. (A) An alignment through the newly defined eIF4GI phospho-region of the members of the human eIF4G family. Locations of defined protein binding sites in eIF4G proteins are indicated, as well as percentage identity to the corresponding region in eIF4GI. Below the diagram is an alignment of the amino acid sequences of eIF4GI, eIF4GII and p97 in this region. Identical residues are boxed in black, similar residues are boxed in gray. (B) Fragments encompassing the phosphorylated region of eIF4GI (aa 1035–1206) and the corresponding regions of eIF4GII (aa 1057–1225) and p97 (aa 395–547) were expressed in 293T cells (5, 10 and 20 μg of DNA transfected) as GST fusion proteins. Cells were metabolically labeled with 32P. Proteins isolated with glutathione-coupled Sepharose beads were washed, gel-purifed, and transferred to nitrocellulose. Upper panel, Western blot using anti-GST antiserum. Lower panel, direct autoradiogram of the same nitrocellulose membrane.

