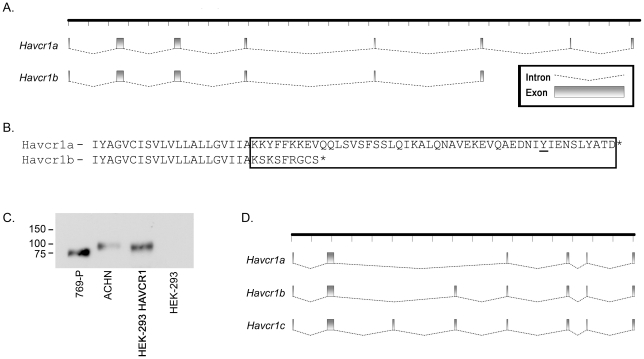
Figure 5. HAVCR1 splice variants.
A. Full-length cDNAs were cloned and sequenced from ε-toxin-sensitive ACHN cells (HAVCR1a) and from ε-toxin-resistant 769-P cells (HAVCR1a and HAVCR1b). The coding-exon structure for each transcript is illustrated. B. Partial amino acid sequences of the HAVCR1a and HAVCR1b proteins are shown; the putative cytoplasmic domains are boxed. A conserved tyrosine present in HAVCR1a, shown previously to become phosphorylated, is underlined [44], [45]. C. Whole-cell lysates were prepared from ε-toxin-sensitive ACHN, from ε-toxin-resistant 769-P and HEK-293 cells, and from HEK-293 cells transfected with a vector expressing HAVCR1a from ACHN cells and analyzed by immunoblot analysis using an anti-HAVCR1 antibody. D. Full-length cDNAs were cloned and sequenced from ε-toxin-sensitive MDCK cells. The coding-exon structures for the three transcripts are illustrated as in “A”.