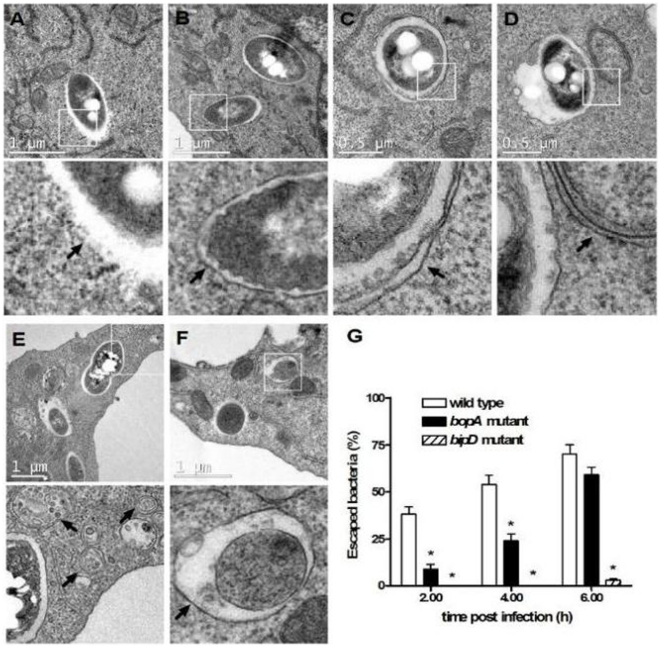
Figure 3. B. pseudomallei-containing vacuoles are bound by single membranes and the TTSS3 and the effector BopA are required for bacterial escape.
(A–F) Transmission electron micrographs show the intracellular location of B. pseudomallei in RAW 264.7 cells at 2–6 h post infection (p.i.). The scale bar is indicated. Boxed areas are shown as magnified images below each panel. Intracellular bacteria were observed either free in the cytosol and not membrane bound (panel A), or within single-membrane phagosomal compartments (panel B). Only one bacterium was found in a double-membrane compartment (panel C), which could be an autophagosome. Canonical autophagosomes having a double-membrane were observed in infected and uninfected RAW 264.7 cells (panels D–F). Arrows indicate detailed membrane ultrastructure. (G) The percentage of bacteria free in the cytosol of RAW 264.7 cells following infection with B. pseudomallei wild-type, bopA mutant and the bipD mutant at 2, 4, and 6 h p.i. Data represent the mean ± SEM of three separate experiments (n = 100 bacteria). Where shown * indicates p<0.05 relative to the wild-type strain at each time point.