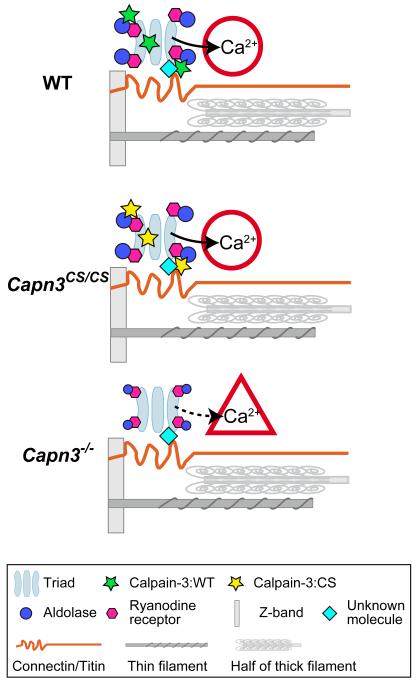
Fig. 6.
Model of calpain-3 structural functions in the SR.
The triads and major myofibrillar components are shown in a half sarcomere. (A) In WT mice, calpain-3 molecules (with proteolytic activity suppressed by an unknown mechanism) are structurally associated with SR components, and normal Ca2+ efflux from the SR takes place. (B) In Capn3CS/CS mice, normal Ca2+ efflux from the SR also takes place because calpain-3:C129S is proteolytically inactive calpain-3 but structurally intact. (C) In Capn3−/− mice, however, the calpain-3 molecules is lost and as a result Ca2+ efflux from the SR is reduced.14