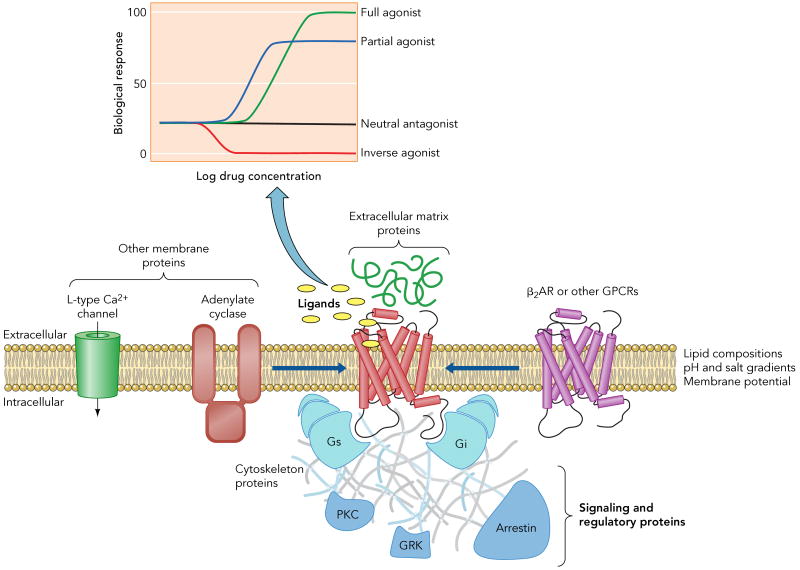
Figure 1. Factors that influence the signaling behavior of the human β2AR.
Ligands with different efficacies (inset) can modulate a given signaling pathway. Moreover, the efficacy of a drug may differ for different down stream signaling profiles. For instance, certain drugs induce routes involving signaling and regulatory proteins (e.g. Gi, arrestin) that complement the predominant pathway through Gs. In addition to ligand binding, other factors as lipid bilayer composition, pH and salt gradients, membrane potential, protein-protein interactions, either within the membrane (homo- or hetero-oligomerization and interaction with other membrane proteins) or with extracellular and intracellular partners, or post-translational modifications, as glycosilation, phosphorylation or acylation, can also influence the signaling behavior of the receptor.