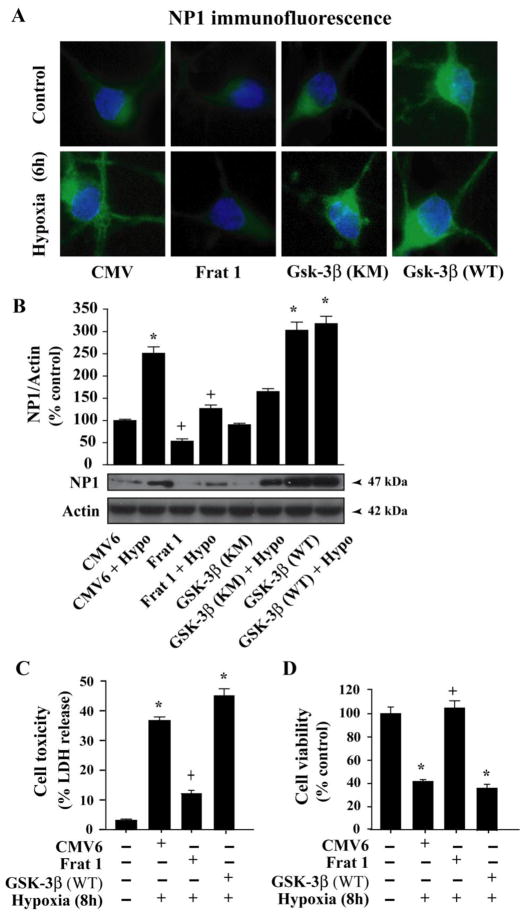
Fig. 8.
Inhibition of GSK-3β function inhibits induction of NP1 in hypoxic-ischemic cortical neurons. Cortical neurons were transfected with control CMV, dominant-negative inhibitor Frat 1,kinase mutant GSK-3β (GSK-3βKM) or WT-GSK-3β (GSK-3βWT) plasmid DNA (2 μg) as described under “Experimental procedures”. Fluorescence microscopy (A) and Western immunoblotting with NP1 antibody showed effective inhibition of GSK-3β by Frat1 that resulted significant decrease in NP1 accumulation. Whereas, overexpression of the GSK-3βWT significantly enhanced NP1 expression. Data represent mean ± SEM (n=4; *p<0.001 vs. control CMV6 and +p <0.001 vs. Frat1 + Hypoxia group. Representative blots are shown. Neuronal death was assessed by LDH release cytotoxicity (C) and MTT reduction cell viability assays (D). Inhibition of GSK-3β significantly reduced cell toxicity and increased cell viability (mean ± SEM, n=8; *p<0.01 vs. control normoxic cells, +p<0.01 vs. hypoxia + control CMV6 transfected group).