Figure 4. Methylation analysis of individual CpG dinucleotides (BDNF exons IV and IX) from the prefrontal cortex of adults with a history of maltreatment or normal maternal care.
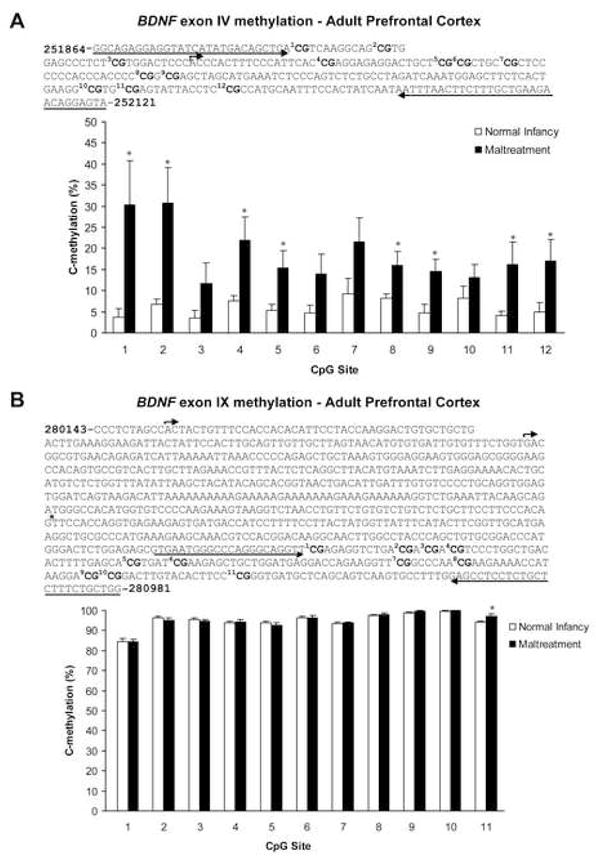
(A) Location of 12 CpG sites relative to the transcription initiation site (bent arrow) of exon IV. Note that this region of exon IV contains a cAMP response element site (TCACGTCA) for transcription factor cAMP response element binding protein, which encompasses CpG site 1. Sequencing primer pair positions are indicated by the left and right arrows, and primer sequences can be found in Supplementary Table 1. Bisulfite DNA sequencing analysis indicates that maltreatment increases methylation of all CpG sites within the examined region of exon IV DNA in the adult prefrontal cortex (two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc tests; significant effect of infant condition F=46.62, p<0.0001). n=7–8/group; *p-values significant versus controls (p 0.05). (B) Location of 11 CpG sites within the common coding exon (IX) relative to two transcription initiation sites (bent arrows) in promoter IXA. *major splice site; sequencing primer pair positions are indicated by the left and right arrows, and primer sequences can be found in Supplementary Table 1. Bisulfite DNA sequencing analysis confirms that maltreatment during infancy results in site-specific methylation of exon IX DNA in the adult prefrontal cortex (n=9–11/group; two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc tests), with a significant increase at CpG site 11 (p=0.0161). For both panels - error bars represent SEM. Male and female adults were derived from 7 mothers.
