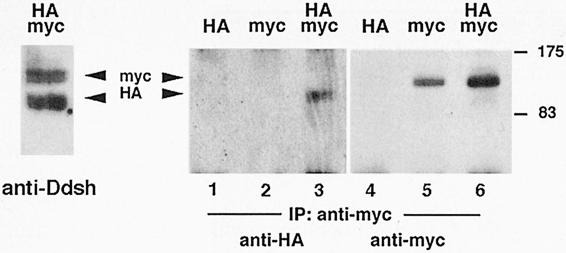
Fig. 8. Biochemical detection of Xdsh homomeric complexes: co-immunoprecipitation of Xdsh-HA and myc-Xdsh. Embryos were injected with either Xdsh-HA (lanes 1 and 4), myc-Xdsh (lanes 2 and 5) or both (lanes 3 and 6) and precipitated with anti-myc antibody, then Western blotted. The blot was first stained with anti-HA antibody (left panel, lanes 1–3), followed by peroxidase inactivation, and restained with anti-myc antibody (right panel, lanes 4–6). Anti-myc antibody precipitates myc-Xdsh of 100 kDa from myc-Xdsh-injected and from co-injected embryos (arrowhead labeled myc in lanes 5 and 6) but not from Xdsh-HA-injected embryos (lanes 1 and 4). Xdsh-HA of 85 kDa (arrowhead labeled HA, lane 3), however, is co-precipitated with anti-myc antibody from embryos co-injected with myc- and HA-tagged Xdsh. The left panel shows an anti-Ddsh stain of longer run myc co-precipitates revealing that both HA and myc-Xdsh contain multiple (phosphorylated) forms. The top of the Figure indicates the mRNA injected: HA is Xdsh-HA, myc is myc-Xdsh, HA/myc is co-injection of Xdsh-HA and myc-Xdsh; the bottom of the Figure shows that anti-myc antibody was used for immunoprecipitation (IP), and staining performed with anti-HA (lanes 1–3) and anti-myc (lanes 4–6) or anti-Drosophila Dsh antibodies (anti-Ddsh, left panel). Standard molecular weights are indicated on the right.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.