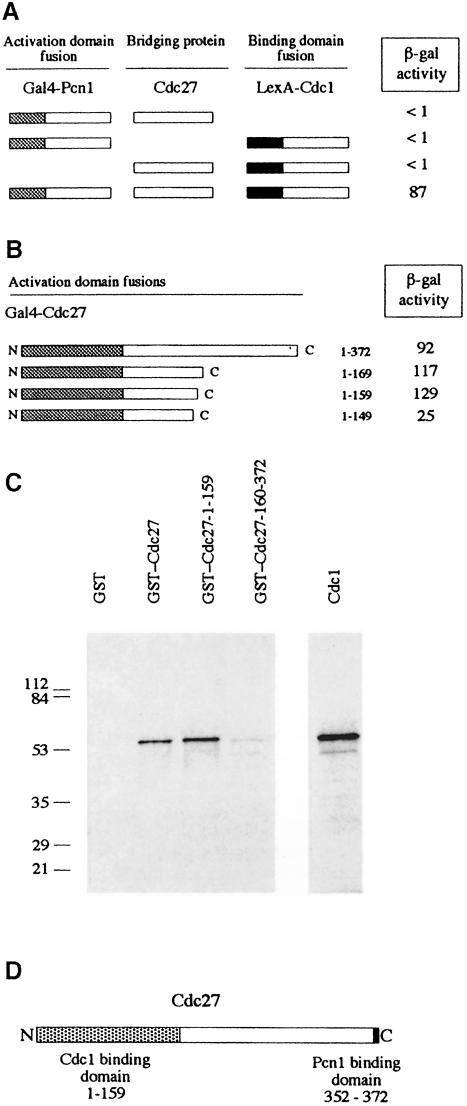
Fig. 7. Distinct N- and C–terminal binding regions for Cdc1 and Pcn1 on Cdc27. (A) Three-component two-hybrid assay. Gal4 AD–Pcn1 and LexA BD–Cdc1 fusions are brought together by simultaneous co-expression of Cdc27. Schematic representation of Gal4 AD–Pcn1 fusions and LexA BD–Cdc1 fusions, with the results of the two-hybrid analysis shown to the right (β-galactosidase activity in liquid cultures expressed in Miller units). (B) Schematic representation of Gal4 AD–Cdc27 fusions used to map the Cdc1 binding domain, with the results of the two-hybrid analysis shown to the right (β-galactosidase activity in liquid cultures expressed in Miller units). (C) In vitro Cdc1–Cdc27 interactions. [35S]methionine-labelled in vitro synthesized Cdc1 was mixed with 5 μg of various GST fusion proteins or with GST alone. Following incubation at room temperature for 3 h, the GST and GST–Cdc27 proteins were re-isolated using glutathione–Sepharose beads. These were washed extensively before being boiled in sample buffer and the sample run on a 12.5% SDS–PAGE gel. Retention of Cdc1 was determined by fluorography. Molecular weight standards are shown to the left of the gel with molecular weights given in kilodaltons. (D) Schematic representation of the Cdc27 protein showing the Cdc1 and Pcn1 binding regions defined in this study.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.