Fig. 1.
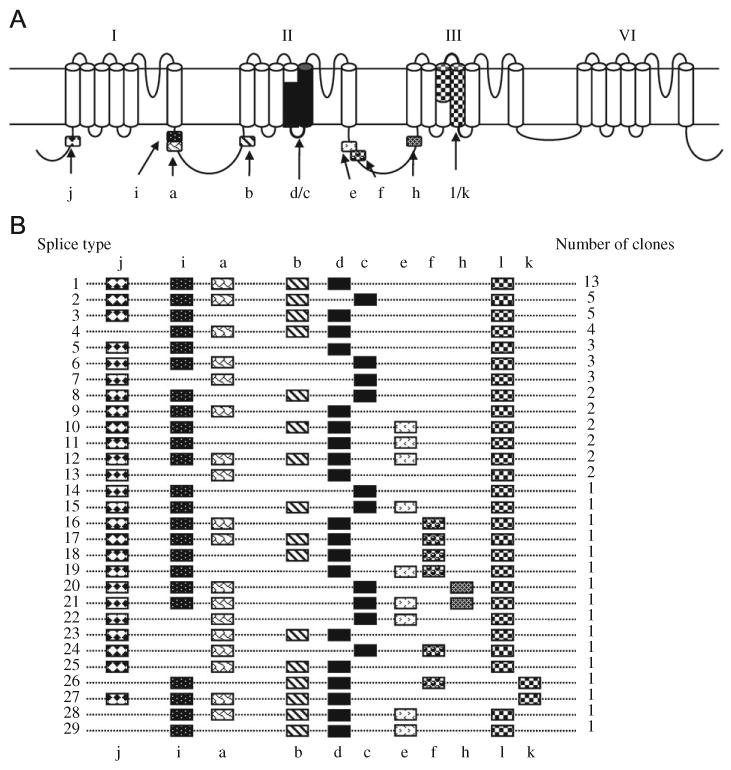
Identification of 29 alternative splice types of the DmNaV transcript. (A) A schematic diagram of the DmNaV sodium channel protein topology, with the positions of alternative exons indicated by patterned boxes. Exons, a, b, i, j, e, f and h are optional, whereas exons c/d and l/k are mutually exclusive. Exons l and k correspond to exons G1 and G2, respectively, in the cockroach BgNav sodium channel (Tan et al., 2002). (B) Schematic presentation of the usage of alternative exons in 64 full-length cDNA clones. The number of clones (i.e., variants) of each splice type is indicated.
