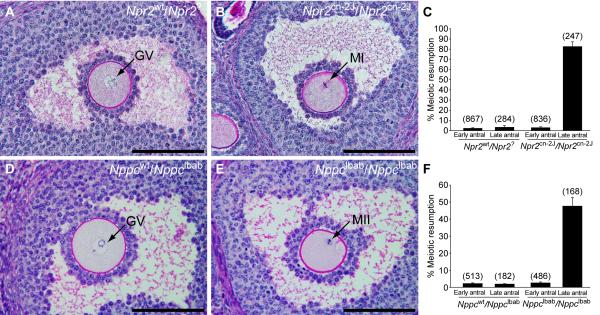
Fig. 3.
Failure to maintain meiotic arrest in Graafian (late antral) follicles of Npr2cn-2J/Npr2cn-2J and Nppclbab/Nppclbab mutant mouse ovaries. (A) A prophase-arrested oocyte (GV indicates germinal vesicle) within a late antral follicle of a control Npr2wt/Npr2? ovary. (B) An oocyte with metaphase I (MI) chromosomes within a late antral follicle of an Npr2cn-2J/Npr2cn-2J mutant ovary. (C) Percentages of oocytes that had resumed meiosis, counted in sections of ovaries from control Npr2wt/Npr2? and mutant Npr2cn-2J/Npr2cn-2J mice that were treated with eCG for 44 hr. Graph shows mean ± SEM of 6 ovaries; numbers above bars indicate number of follicles examined. (D-E) Ovarian follicles after development as grafts under kidney capsules of immunodeficient hosts for 30 days. (D) A prophase-arrested oocyte within a late antral follicle of a heterozygous control Nppcwt/Nppclbab ovary. (E) An oocyte with metaphase II (MII) chromosomes and a polar body, within a late antral follicle of a mutant Nppclbab/Nppclbab ovary. (F) Percentages of oocytes that had resumed meiosis, counted in sections of Nppcwt/Nppclbab and Nppclbab/Nppclbab grafted ovaries. Graph shows mean ± SEM of 6 ovaries; numbers above bars indicate number of follicles examined. The terms “Early” and “Late” antral follicles are used as defined by Pedersen and Peters (15). Bars = 100 μm.