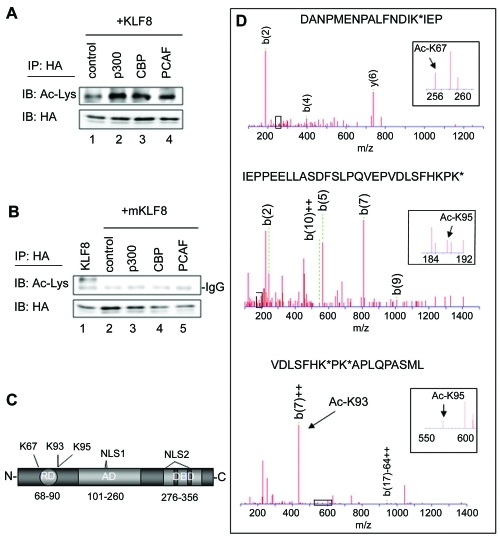
Figure 1.
KLF8 is acetylated by p300, CBP and PCAF at lysines 67, 93 and 95. (A) p300, CBP, and PCAF promote KLF8 acetylation. HEK293 cells were transfected with HA-KLF8 and either empty vector control, p300, CBP, or PCAF. Lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) using an anti-HA antibody and blotted (IB) using an anti-acetyl lysine or anti-HA antibody. (B) KLF8 cannot be acetylated when it does not interact with co-activators. Experiments were performed similarly as in A, but the Q118N-Q248N-KLF8 mutant that cannot bind to the co-activators (mKLF8) was transfected with empty vector control or with p300, CBP, or PCAF. Expression of the transfected constructs was verified by whole cell lysate blotting (data not shown). (C) Schematic diagram of KLF8, C-terminal DNA binding domain (DBD), non-classical nuclear localization signals (NLS1&2), N-terminal repression domain (RD), and a centrally located activation domain (AD). The amino acid location of each domain is indicated below. The location of lysines 67, 93, and 95 is also indicated. (D) Mass spectrometry identification of acetylated residues. Immunoprecipitated HA-KLF8 was resolved on an SDS-PAGE gel, stained with Coomassie (data not shown), digested with chymotrypsin or trypsin and prepared for mass spectrometry analysis as described in Materials and Methods. N-terminal b ions or C-terminal y ions were analyzed using the Mascot software. The identified peptide sequence and its MS/MS spectrum of fragmentation when cells were co-transfected with KLF8 and PCAF (top and middle) or KLF8 and p300 (bottom) are depicted. Inset: peaks that represent a lysine with the 42 dalton additional mass representative of an acetylated state. *=acetylated lysines, m/z=massto charge ratio.